Aparté sur le voyageur de commerce¶
Le voyageur de commerce ou Travelling Salesman Problem en anglais est le problème NP-complet emblématique : il n’existe pas d’algorithme capable de trouver la solution optimale en temps polynômial. La seule option est de parcourir toutes les configurations pour trouver la meilleure. Ce notebook ne fait qu’aborder le problème.
[1]:
%matplotlib inline
Tirer des points aléatoirement et les afficher¶
[2]:
import numpy
points = numpy.random.random((6, 2))
points
[2]:
array([[0.20256988, 0.27603738],
[0.77763596, 0.50108287],
[0.07482647, 0.60880805],
[0.56075455, 0.9637854 ],
[0.79735982, 0.32773718],
[0.65017942, 0.96827692]])
Distance d’un chemin¶
[3]:
def distance_chemin(points, chemin):
dist = 0
for i in range(1, len(points)):
dx, dy = points[chemin[i], :] - points[chemin[i - 1], :]
dist += (dx**2 + dy**2) ** 0.5
dx, dy = points[chemin[0], :] - points[chemin[-1], :]
dist += (dx**2 + dy**2) ** 0.5
return dist
distance_chemin(points, list(range(points.shape[0])))
[3]:
4.090536785820115
Visualisation¶
[4]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_points(points, chemin):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(8, 4))
loop = list(chemin) + [chemin[0]]
p = points[loop]
ax[0].plot(points[:, 0], points[:, 1], "o")
ax[1].plot(p[:, 0], p[:, 1], "o-")
ax[1].set_title("dist=%1.2f" % distance_chemin(points, chemin))
return ax
plot_points(points, list(range(points.shape[0])));
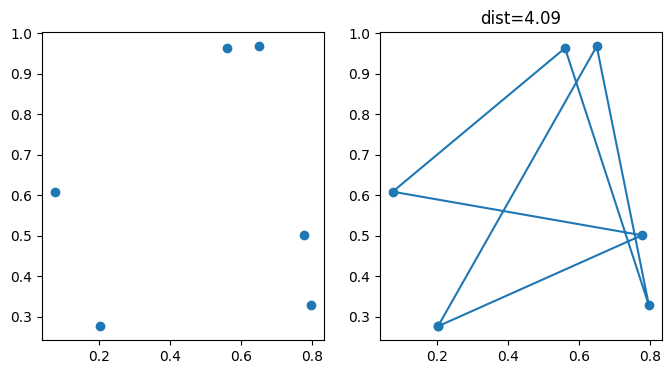
Parcourir toutes les permutations¶
[5]:
from itertools import permutations
def optimisation(points, chemin):
dist = distance_chemin(points, chemin)
best = chemin
for perm in permutations(chemin):
d = distance_chemin(points, perm)
if d < dist:
dist = d
best = perm
return best
res = optimisation(points, list(range(points.shape[0])))
plot_points(points, res);
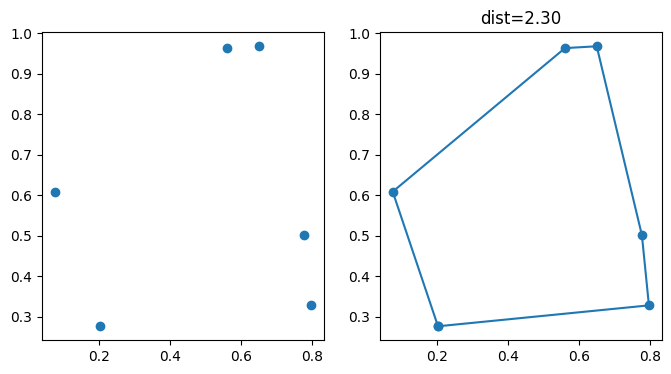
Module tqdm¶
Utile seulement dans un notebook, très utile pour les impatients.
[6]:
from tqdm import tqdm
def optimisation(points, chemin):
dist = distance_chemin(points, chemin)
best = chemin
loop = tqdm(permutations(chemin))
for perm in loop:
loop.set_description(str(perm))
d = distance_chemin(points, perm)
if d < dist:
dist = d
best = perm
return best
res = optimisation(points, list(range(points.shape[0])))
plot_points(points, res);
(0, 1, 3, 5, 2, 4): : 0it [00:00, ?it/s](5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0): : 720it [00:03, 227.89it/s]
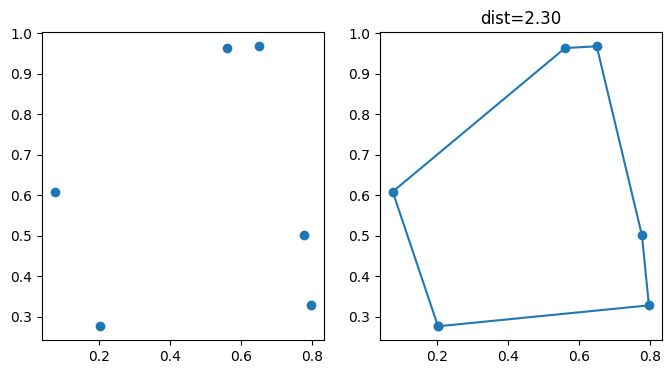
Retournement¶
Les permutations ça prend du temps même avec les machines d’aujourd’hui.
[7]:
def optimisation_retournement(points, chemin):
dist = distance_chemin(points, chemin)
best = chemin
for i in range(1, len(chemin)):
for j in range(i + 1, len(chemin)):
chemin[i:j] = chemin[j - 1 : i - 1 : -1]
d = distance_chemin(points, chemin)
if d < dist:
dist = d
else:
chemin[i:j] = chemin[j - 1 : i - 1 : -1]
return chemin
res = optimisation_retournement(points, list(range(points.shape[0])))
plot_points(points, res);
[ ]: