Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
101: Linear Regression and export to ONNX¶
scikit-learn and torch to train a linear regression.
data¶
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, SGDRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import torch
from onnxruntime import InferenceSession
from experimental_experiment.helpers import pretty_onnx
from onnx_array_api.plotting.graphviz_helper import plot_dot
from experimental_experiment.torch_interpreter import to_onnx
X, y = make_regression(1000, n_features=5, noise=10.0, n_informative=2)
print(X.shape, y.shape)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y)
(1000, 5) (1000,)
scikit-learn: the simple regression¶
clr = LinearRegression()
clr.fit(X_train, y_train)
print(f"coefficients: {clr.coef_}, {clr.intercept_}")
coefficients: [69.02195925 -0.66433185 0.19923977 82.10065227 -0.37140883], -0.05722462622375368
Evaluation¶
LinearRegression: l2=91.36966607433862, r2=0.9926788150765894
scikit-learn: SGD algorithm¶
SGD = Stochastic Gradient Descent
clr = SGDRegressor(max_iter=5, verbose=1)
clr.fit(X_train, y_train)
print(f"coefficients: {clr.coef_}, {clr.intercept_}")
-- Epoch 1
Norm: 91.63, NNZs: 5, Bias: -0.286900, T: 750, Avg. loss: 1244.551555, Objective: 1244.780864
Total training time: 0.00 seconds.
-- Epoch 2
Norm: 103.14, NNZs: 5, Bias: -0.266917, T: 1500, Avg. loss: 93.776593, Objective: 94.263491
Total training time: 0.00 seconds.
-- Epoch 3
Norm: 106.13, NNZs: 5, Bias: -0.060744, T: 2250, Avg. loss: 53.161536, Objective: 53.709504
Total training time: 0.00 seconds.
-- Epoch 4
Norm: 106.91, NNZs: 5, Bias: -0.155506, T: 3000, Avg. loss: 50.252138, Objective: 50.819723
Total training time: 0.00 seconds.
-- Epoch 5
Norm: 107.08, NNZs: 5, Bias: -0.107755, T: 3750, Avg. loss: 49.981113, Objective: 50.554201
Total training time: 0.00 seconds.
~/vv/this312/lib/python3.12/site-packages/sklearn/linear_model/_stochastic_gradient.py:1612: ConvergenceWarning: Maximum number of iteration reached before convergence. Consider increasing max_iter to improve the fit.
warnings.warn(
coefficients: [68.95099995 -0.6219699 0.18463212 81.92761404 -0.2993743 ], [-0.10775536]
Evaluation
SGDRegressor: sl2=91.35556316944299, sr2=0.9926799451012369
Linrar Regression with pytorch¶
class TorchLinearRegression(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_dims: int, n_targets: int):
super().__init__()
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(n_dims, n_targets)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x)
def train_loop(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
total_loss = 0.0
# Set the model to training mode - important for batch normalization and dropout layers
# Unnecessary in this situation but added for best practices
model.train()
for X, y in dataloader:
# Compute prediction and loss
pred = model(X)
loss = loss_fn(pred.ravel(), y)
# Backpropagation
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
# training loss
total_loss += loss
return total_loss
model = TorchLinearRegression(X_train.shape[1], 1)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
loss_fn = torch.nn.MSELoss()
device = "cpu"
model = model.to(device)
dataset = torch.utils.data.TensorDataset(
torch.Tensor(X_train).to(device), torch.Tensor(y_train).to(device)
)
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=1)
for i in range(5):
loss = train_loop(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer)
print(f"iteration {i}, loss={loss}")
iteration 0, loss=2862736.25
iteration 1, loss=198890.625
iteration 2, loss=80917.5234375
iteration 3, loss=75465.203125
iteration 4, loss=75179.75
Let’s check the error
TorchLinearRegression: tl2=91.20539994296203, tr2=0.9926919772427232
And the coefficients.
print("coefficients:")
for p in model.parameters():
print(p)
coefficients:
Parameter containing:
tensor([[68.8545, -0.3939, 0.1367, 82.0421, -0.3821]], requires_grad=True)
Parameter containing:
tensor([0.0433], requires_grad=True)
Conversion to ONNX¶
Let’s convert it to ONNX.
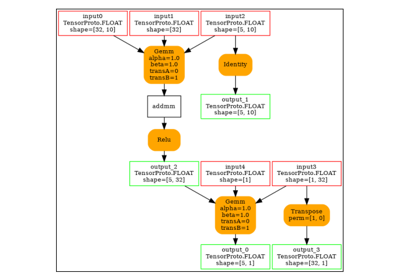
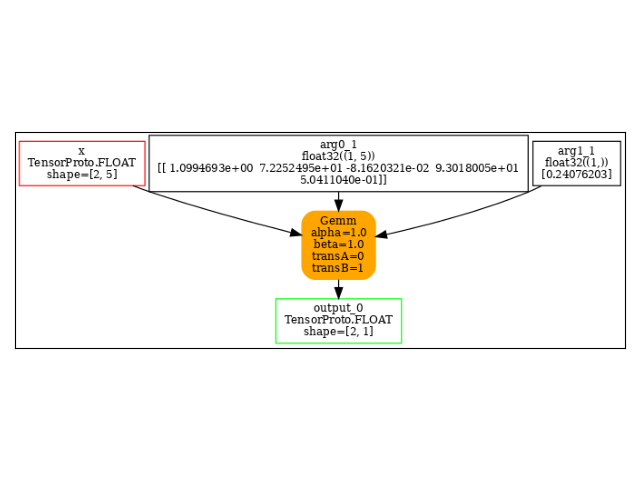
onx = to_onnx(model, (torch.Tensor(X_test[:2]),), input_names=["x"])
Let’s check it is work.
sess = InferenceSession(onx.SerializeToString(), providers=["CPUExecutionProvider"])
res = sess.run(None, {"x": X_test.astype(np.float32)[:2]})
print(res)
[array([[ 13.047354],
[242.91374 ]], dtype=float32)]
And the model.
With dynamic shapes¶
The dynamic shapes are used by torch.export.export() and must
follow the convention described there. The dynamic dimension allows
any value. The model is then valid for many different shapes.
That’s usually what users need.
onx = to_onnx(
model,
(torch.Tensor(X_test[:2]),),
input_names=["x"],
dynamic_shapes={"x": {0: torch.export.Dim("batch")}},
)
print(pretty_onnx(onx))
opset: domain='' version=18
input: name='x' type=dtype('float32') shape=['batch', 5]
init: name='GemmTransposePattern--p_linear_weight::T10' type=float32 shape=(1, 5)-- GraphBuilder.constant_folding.from/fold(init7_s2_1_5,p_linear_weight::T10)##p_linear_weight::T10/GraphBuilder.constant_folding.from/fold(p_linear_weight)##p_linear_weight/DynamoInterpret.placeholder.1/P(linear.weight)##init7_s2_1_5/TransposeEqualReshapePattern.apply.new_shape
init: name='linear.bias' type=float32 shape=(1,) -- array([0.04327609], dtype=float32)-- DynamoInterpret.placeholder.1/P(linear.bias)
Gemm(x, GemmTransposePattern--p_linear_weight::T10, linear.bias, transB=1) -> output_0
output: name='output_0' type=dtype('float32') shape=['batch', 1]
For simplicity, it is possible to use torch.export.Dim.DYNAMIC
or torch.export.Dim.AUTO.
onx = to_onnx(
model,
(torch.Tensor(X_test[:2]),),
input_names=["x"],
dynamic_shapes={"x": {0: torch.export.Dim.DYNAMIC}},
)
print(pretty_onnx(onx))
opset: domain='' version=18
input: name='x' type=dtype('float32') shape=['batch', 5]
init: name='GemmTransposePattern--p_linear_weight::T10' type=float32 shape=(1, 5)-- GraphBuilder.constant_folding.from/fold(init7_s2_1_5,p_linear_weight::T10)##p_linear_weight::T10/GraphBuilder.constant_folding.from/fold(p_linear_weight)##p_linear_weight/DynamoInterpret.placeholder.1/P(linear.weight)##init7_s2_1_5/TransposeEqualReshapePattern.apply.new_shape
init: name='linear.bias' type=float32 shape=(1,) -- array([0.04327609], dtype=float32)-- DynamoInterpret.placeholder.1/P(linear.bias)
Gemm(x, GemmTransposePattern--p_linear_weight::T10, linear.bias, transB=1) -> output_0
output: name='output_0' type=dtype('float32') shape=['batch', 1]
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 5.601 seconds)
Related examples
201: Use torch to export a scikit-learn model into ONNX
201: Evaluate different ways to export a torch model to ONNX
101: Onnx Model Optimization based on Pattern Rewriting