Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Measuring CUDA performance with a vector addition with streams¶
Measure the time between two additions, with or without streams. The script can be profiled with Nsight.
nsys profile python _doc/examples/plot_bench_cuda_vector_add_stream.py
Vector Add¶
from tqdm import tqdm
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pandas import DataFrame
from teachcompute.ext_test_case import measure_time, unit_test_going
import torch
has_cuda = torch.cuda.is_available()
try:
from teachcompute.validation.cuda.cuda_example_py import (
vector_add,
vector_add_stream,
)
except ImportError:
has_cuda = False
def cuda_vector_add(values):
torch.cuda.nvtx.range_push(f"CUDA dim={values.size}")
res = vector_add(values, values, 0, repeat=10)
torch.cuda.nvtx.range_pop()
return res
def cuda_vector_add_stream(values):
torch.cuda.nvtx.range_push(f"CUDA stream dim={values.size}")
res = vector_add_stream(values, values, 0, repeat=10)
torch.cuda.nvtx.range_pop()
return res
obs = []
dims = [2**10, 2**15, 2**20]
if unit_test_going():
dims = [10, 20, 30]
for dim in tqdm(dims):
values = numpy.ones((dim,), dtype=numpy.float32).ravel()
if has_cuda:
diff = numpy.abs(vector_add(values, values, 0) - (values + values)).max()
res = measure_time(lambda values=values: cuda_vector_add(values), max_time=0.5)
obs.append(
dict(
dim=dim,
size=values.size,
time=res["average"],
fct="CUDA",
time_per_element=res["average"] / dim,
diff=diff,
)
)
diff = numpy.abs(vector_add_stream(values, values, 0) - (values + values)).max()
res = measure_time(
lambda values=values: cuda_vector_add_stream(values), max_time=0.5
)
obs.append(
dict(
dim=dim,
size=values.size,
time=res["average"],
fct="CUDA-stream",
time_per_element=res["average"] / dim,
diff=diff,
)
)
if has_cuda:
df = DataFrame(obs)
piv = df.pivot(index="dim", columns="fct", values="time_per_element")
print(piv)
0%| | 0/3 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
33%|███▎ | 1/3 [00:01<00:02, 1.27s/it]
67%|██████▋ | 2/3 [00:02<00:01, 1.33s/it]
100%|██████████| 3/3 [00:03<00:00, 1.32s/it]
100%|██████████| 3/3 [00:03<00:00, 1.32s/it]
fct CUDA CUDA-stream
dim
1024 4.850350e-06 5.337401e-06
32768 1.234465e-07 1.848561e-07
1048576 1.771046e-08 1.865589e-08
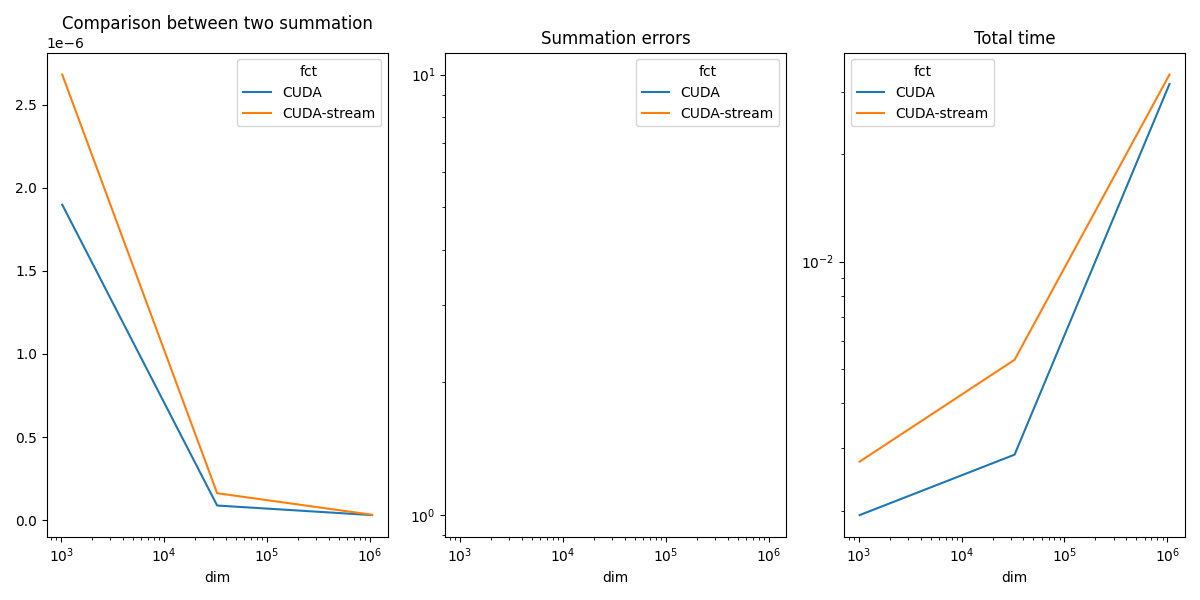
Plots¶
if has_cuda:
piv_diff = df.pivot(index="dim", columns="fct", values="diff")
piv_time = df.pivot(index="dim", columns="fct", values="time")
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(12, 6))
piv.plot(ax=ax[0], logx=True, title="Comparison between two summation")
piv_diff.plot(ax=ax[1], logx=True, logy=True, title="Summation errors")
piv_time.plot(ax=ax[2], logx=True, logy=True, title="Total time")
fig.tight_layout()
fig.savefig("plot_bench_cuda_vector_add_stream.png")
~/vv/this312/lib/python3.12/site-packages/pandas/plotting/_matplotlib/core.py:822: UserWarning: Data has no positive values, and therefore cannot be log-scaled.
labels = axis.get_majorticklabels() + axis.get_minorticklabels()
In practice, one stream is usually enough. CUDA parallelizes everything and takes all the computing power.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 5.009 seconds)