Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
101: A custom backend for torch¶
This example leverages the examples introduced on this page
Custom Backends.
It uses backend experimental_experiment.torch_dynamo.onnx_custom_backend()
based on onnxruntime and running on CPU or CUDA.
It could easily replaced by
experimental_experiment.torch_dynamo.onnx_debug_backend().
This one based on the reference implemented from onnx
can show the intermediate results if needed. It is very slow.
A model¶
import copy
from experimental_experiment.helpers import pretty_onnx
from onnx_array_api.plotting.graphviz_helper import plot_dot
import torch
from torch._dynamo.backends.common import aot_autograd
# from torch._functorch._aot_autograd.utils import make_boxed_func
from experimental_experiment.torch_dynamo import (
onnx_custom_backend,
get_decomposition_table,
)
from experimental_experiment.torch_interpreter import ExportOptions
class MLP(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.layers = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(10, 32),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(32, 1),
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.layers(x)
x = torch.randn(3, 10, dtype=torch.float32)
mlp = MLP()
print(mlp(x))
tensor([[-0.1528],
[-0.0814],
[ 0.0829]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>)
A custom backend¶
This backend leverages onnxruntime.
It is available through function
experimental_experiment.torch_dynamo.onnx_custom_backend()
and implemented by class OrtBackend.
compiled_model = torch.compile(
copy.deepcopy(mlp),
backend=lambda *args, **kwargs: onnx_custom_backend(*args, target_opset=18, **kwargs),
dynamic=False,
fullgraph=True,
)
print(compiled_model(x))
tensor([[-0.1528],
[-0.0814],
[ 0.0829]])
Training¶
It can be used for training as well. The compilation may not
be working if the model is using function the converter does not know.
Maybe, there exist a way to decompose this new function into
existing functions. A recommended list is returned by
with function get_decomposition_table.
An existing list can be filtered out from some inefficient decompositions
with function filter_decomposition_table.
aot_compiler = aot_autograd(
fw_compiler=lambda *args, **kwargs: onnx_custom_backend(
*args,
target_opset=18,
export_options=ExportOptions(decomposition_table=get_decomposition_table()),
**kwargs,
),
)
compiled_model = torch.compile(
copy.deepcopy(mlp),
backend=aot_compiler,
fullgraph=True,
dynamic=False,
)
print(compiled_model(x))
tensor([[-0.1528],
[-0.0814],
[ 0.0829]], grad_fn=<CompiledFunctionBackward>)
Let’s see an iteration loop.
from sklearn.datasets import load_diabetes
class DiabetesDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, X, y):
self.X = torch.from_numpy(X / 10).to(torch.float32)
self.y = torch.from_numpy(y).to(torch.float32).reshape((-1, 1))
def __len__(self):
return len(self.X)
def __getitem__(self, i):
return self.X[i], self.y[i]
def trained_model(max_iter=5, dynamic=False, storage=None):
aot_compiler = aot_autograd(
fw_compiler=lambda *args, **kwargs: onnx_custom_backend(
*args, target_opset=18, storage=storage, **kwargs
),
decompositions=get_decomposition_table(),
)
compiled_model = torch.compile(
MLP(),
backend=aot_compiler,
fullgraph=True,
dynamic=dynamic,
)
trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
DiabetesDataset(*load_diabetes(return_X_y=True)),
batch_size=5,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=0,
)
loss_function = torch.nn.L1Loss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(compiled_model.parameters(), lr=1e-1)
for epoch in range(0, max_iter):
current_loss = 0.0
for _, data in enumerate(trainloader, 0):
X, y = data
optimizer.zero_grad()
p = compiled_model(X)
loss = loss_function(p, y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
current_loss += loss.item()
print(f"Loss after epoch {epoch+1}: {current_loss}")
print("Training process has finished.")
return compiled_model
trained_model(3)
~/vv/this312/lib/python3.12/site-packages/torch/_functorch/_aot_autograd/utils.py:130: UserWarning: Your compiler for AOTAutograd is returning a function that doesn't take boxed arguments. Please wrap it with functorch.compile.make_boxed_func or handle the boxed arguments yourself. See https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/83137#issuecomment-1211320670 for rationale.
warnings.warn(
~/vv/this312/lib/python3.12/site-packages/torch/_functorch/_aot_autograd/utils.py:130: UserWarning: Your compiler for AOTAutograd is returning a function that doesn't take boxed arguments. Please wrap it with functorch.compile.make_boxed_func or handle the boxed arguments yourself. See https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/83137#issuecomment-1211320670 for rationale.
warnings.warn(
Loss after epoch 1: 7453.071088790894
Loss after epoch 2: 5568.628337860107
Loss after epoch 3: 5265.660064697266
Training process has finished.
OptimizedModule(
(_orig_mod): MLP(
(layers): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=32, bias=True)
(1): ReLU()
(2): Linear(in_features=32, out_features=1, bias=True)
)
)
)
What about the ONNX model?¶
The backend converts the model into ONNX then runs it with onnxruntime. Let’s see what it looks like.
~/vv/this312/lib/python3.12/site-packages/torch/_functorch/_aot_autograd/utils.py:130: UserWarning: Your compiler for AOTAutograd is returning a function that doesn't take boxed arguments. Please wrap it with functorch.compile.make_boxed_func or handle the boxed arguments yourself. See https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/83137#issuecomment-1211320670 for rationale.
warnings.warn(
~/vv/this312/lib/python3.12/site-packages/torch/_functorch/_aot_autograd/utils.py:130: UserWarning: Your compiler for AOTAutograd is returning a function that doesn't take boxed arguments. Please wrap it with functorch.compile.make_boxed_func or handle the boxed arguments yourself. See https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/83137#issuecomment-1211320670 for rationale.
warnings.warn(
Loss after epoch 1: 7458.868743896484
Loss after epoch 2: 5491.478296279907
Loss after epoch 3: 5199.069602966309
Training process has finished.
4 were created.
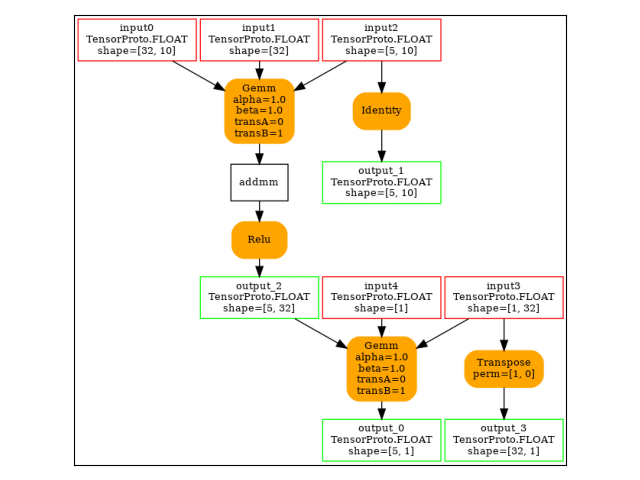
-- model 0 running on ['CPUExecutionProvider']
opset: domain='' version=18
input: name='input0' type=dtype('float32') shape=[32, 10]
input: name='input1' type=dtype('float32') shape=[32]
input: name='input2' type=dtype('float32') shape=[5, 10]
input: name='input3' type=dtype('float32') shape=[1, 32]
input: name='input4' type=dtype('float32') shape=[1]
init: name='init7_s2_-1_1' type=int64 shape=(2,) -- array([-1, 1]) -- TransposeEqualReshapePattern.apply.new_shape
Gemm(input2, input0, input1, transA=0, transB=1, alpha=1.00, beta=1.00) -> addmm
Relu(addmm) -> output_2
Reshape(input3, init7_s2_-1_1) -> output_3
Gemm(output_2, output_3, input4, alpha=1.00, beta=1.00) -> output_0
Identity(input2) -> output_1
output: name='output_0' type=dtype('float32') shape=[5, 1]
output: name='output_1' type=dtype('float32') shape=[5, 10]
output: name='output_2' type=dtype('float32') shape=[5, 32]
output: name='output_3' type=dtype('float32') shape=[32, 1]
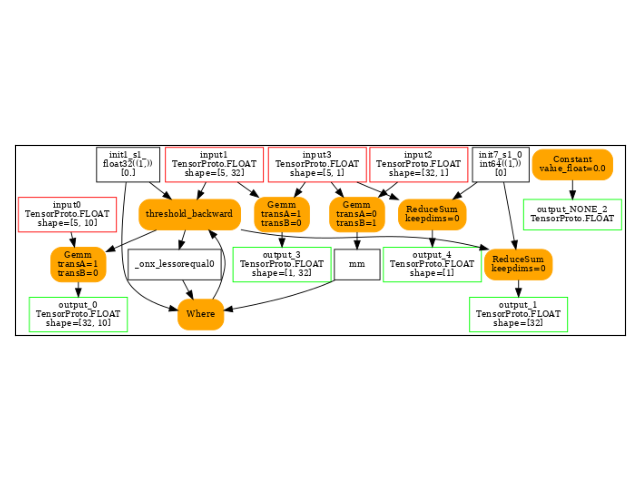
-- model 1 running on ['CPUExecutionProvider']
opset: domain='' version=18
input: name='input0' type=dtype('float32') shape=[5, 10]
input: name='input1' type=dtype('float32') shape=[5, 32]
input: name='input2' type=dtype('float32') shape=[32, 1]
input: name='input3' type=dtype('float32') shape=[5, 1]
init: name='init7_s1_0' type=int64 shape=(1,) -- array([0]) -- Opset.make_node.1/Shape##Opset.make_node.1/Shape
init: name='init1_s1_' type=float32 shape=(1,) -- array([0.], dtype=float32)-- Opset.make_node.1/Small##Opset.make_node.1/Small
init: name='init7_s2_1_-1' type=int64 shape=(2,) -- array([ 1, -1]) -- TransposeEqualReshapePattern.apply.new_shape##TransposeEqualReshapePattern.apply.new_shape
Constant(value_float=0.0) -> output_NONE_2
Reshape(input2, init7_s2_1_-1) -> t_2
MatMul(input3, t_2) -> mm
Reshape(input3, init7_s2_1_-1) -> t_3
MatMul(t_3, input1) -> output_3
ReduceSum(input3, init7_s1_0, keepdims=0) -> output_4
LessOrEqual(input1, init1_s1_) -> _onx_lessorequal_detach_30
Where(_onx_lessorequal_detach_30, init1_s1_, mm) -> threshold_backward
Gemm(threshold_backward, input0, transA=1, transB=0) -> output_0
ReduceSum(threshold_backward, init7_s1_0, keepdims=0) -> output_1
output: name='output_0' type=dtype('float32') shape=[32, 10]
output: name='output_1' type=dtype('float32') shape=[32]
output: name='output_NONE_2' type=dtype('float32') shape=None
output: name='output_3' type=dtype('float32') shape=[1, 32]
output: name='output_4' type=dtype('float32') shape=[1]
The forward graph.
The backward graph.
What about dynamic shapes?¶
Any input or output having _dim_ in its name is a dynamic dimension. Any output having _NONE_ in its name is replace by None. It is needed by pytorch.
~/vv/this312/lib/python3.12/site-packages/torch/_functorch/_aot_autograd/utils.py:130: UserWarning: Your compiler for AOTAutograd is returning a function that doesn't take boxed arguments. Please wrap it with functorch.compile.make_boxed_func or handle the boxed arguments yourself. See https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/83137#issuecomment-1211320670 for rationale.
warnings.warn(
Loss after epoch 1: 7439.707229614258
Loss after epoch 2: 5489.145149230957
Loss after epoch 3: 5245.902578353882
Training process has finished.
2 were created.
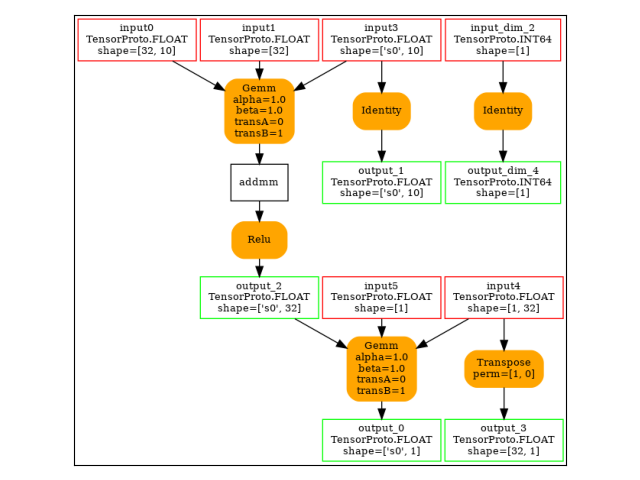
-- model 0 running on ['CPUExecutionProvider']
opset: domain='' version=18
input: name='input0' type=dtype('float32') shape=[32, 10]
input: name='input1' type=dtype('float32') shape=[32]
input: name='input_dim_2' type=dtype('int64') shape=None
input: name='input3' type=dtype('float32') shape=['s0', 10]
input: name='input4' type=dtype('float32') shape=[1, 32]
input: name='input5' type=dtype('float32') shape=[1]
init: name='init7_s2_-1_1' type=int64 shape=(2,) -- array([-1, 1]) -- TransposeEqualReshapePattern.apply.new_shape
Gemm(input3, input0, input1, transA=0, transB=1, alpha=1.00, beta=1.00) -> addmm
Relu(addmm) -> output_2
Reshape(input4, init7_s2_-1_1) -> output_3
Gemm(output_2, output_3, input5, alpha=1.00, beta=1.00) -> output_0
Identity(input3) -> output_1
Identity(input_dim_2) -> output_dim_4
output: name='output_0' type=dtype('float32') shape=['s0', 1]
output: name='output_1' type=dtype('float32') shape=['s0', 10]
output: name='output_2' type=dtype('float32') shape=['s0', 32]
output: name='output_3' type=dtype('float32') shape=[32, 1]
output: name='output_dim_4' type=dtype('int64') shape=None
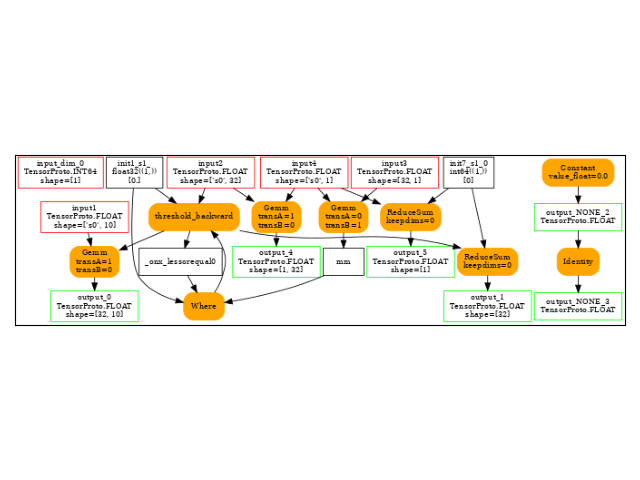
-- model 1 running on ['CPUExecutionProvider']
opset: domain='' version=18
input: name='input_dim_0' type=dtype('int64') shape=None
input: name='input1' type=dtype('float32') shape=['s0', 10]
input: name='input2' type=dtype('float32') shape=['s0', 32]
input: name='input3' type=dtype('float32') shape=[32, 1]
input: name='input4' type=dtype('float32') shape=['s0', 1]
init: name='init7_s1_0' type=int64 shape=(1,) -- array([0]) -- Opset.make_node.1/Shape##Opset.make_node.1/Shape
init: name='init1_s1_' type=float32 shape=(1,) -- array([0.], dtype=float32)-- Opset.make_node.1/Small##Opset.make_node.1/Small
init: name='init7_s2_1_-1' type=int64 shape=(2,) -- array([ 1, -1]) -- TransposeEqualReshapePattern.apply.new_shape##TransposeEqualReshapePattern.apply.new_shape
Constant(value_float=0.0) -> output_NONE_2
Identity(output_NONE_2) -> output_NONE_3
Reshape(input3, init7_s2_1_-1) -> t_2
MatMul(input4, t_2) -> mm
Reshape(input4, init7_s2_1_-1) -> t_3
MatMul(t_3, input2) -> output_4
ReduceSum(input4, init7_s1_0, keepdims=0) -> output_5
LessOrEqual(input2, init1_s1_) -> _onx_lessorequal_detach_30
Where(_onx_lessorequal_detach_30, init1_s1_, mm) -> threshold_backward
Gemm(threshold_backward, input1, transA=1, transB=0) -> output_0
ReduceSum(threshold_backward, init7_s1_0, keepdims=0) -> output_1
output: name='output_0' type=dtype('float32') shape=[32, 10]
output: name='output_1' type=dtype('float32') shape=[32]
output: name='output_NONE_2' type=dtype('float32') shape=None
output: name='output_NONE_3' type=dtype('float32') shape=None
output: name='output_4' type=dtype('float32') shape=[1, 32]
output: name='output_5' type=dtype('float32') shape=[1]
The forward graph.
The backward graph.
Pattern Optimizations¶
By default, once exported into onnx, a model is optimized by looking for patterns. Each of them locally replaces a couple of nodes to optimize the computation (see .xoptim.patterns and .xoptim.patterns_ort).
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 19.443 seconds)
Related examples
101: Onnx Model Optimization based on Pattern Rewriting