Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Converting torch.histc into ONNX¶
torch.histc() computes an histogram of a tensor,
it counts the number of elements falling into each bin.
There are many options do to this. If the number of bins
is not too high, we can use something based on braodcasting.
This method implies the creation of a matrix
where N is the number of elements in a tensor and B the number
if bins. To avoid this, the best way is to use a tree.
Before doing that, let’s first study
torch.histc().
See issue 174668.
float32 and float16¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
def create_input(dtype, hmin, hmax):
inf = torch.tensor(torch.inf, dtype=torch.float16)
buffer = torch.tensor([hmin], dtype=torch.float16)
res = []
while buffer[0] <= hmax:
buffer = torch.nextafter(buffer, inf)
res.append(buffer[0])
return torch.tensor(res, dtype=dtype)
hbins, hmin, hmax = 20, -5, 5
dtype = torch.float16
tensor = create_input(dtype, hmin, hmax)
print(f"There are {tensor.shape} elements in [{hmin}, {hmax}] of type {torch.float16}).")
There are torch.Size([35329]) elements in [-5, 5] of type torch.float16).
histc
hist=tensor([ 127., 128., 256., 256., 256., 256., 511., 512., 1021.,
5224., 12480., 1028., 514., 512., 257., 256., 255., 256.,
129., 130.], dtype=torch.float16)
We can see there are more elements in the center.
def torch_histc_equivalent(tensor, bins, fmin, fmax, thresholds=None):
# thresholds
if thresholds is None:
delta = (float(fmax) - float(fmin)) / float(bins)
inf = torch.tensor(torch.inf, dtype=tensor.dtype)
delta = torch.tensor(delta, dtype=tensor.dtype)
min = torch.tensor(fmin, dtype=tensor.dtype)
max = torch.tensor(fmax, dtype=tensor.dtype)
bins = int(bins)
thresholds = torch.zeros((bins + 1,), dtype=tensor.dtype)
halfway = bins + 1 - (bins + 1) // 2
for i in range(halfway):
thresholds[i] = min + delta * i
for i in range(halfway, bins + 1):
thresholds[i] = max - delta * (bins - i)
thresholds[-1] = torch.nextafter(thresholds[-1], inf)
# computation
value = thresholds.unsqueeze(1) < tensor.reshape((-1,)).unsqueeze(0)
value = value.sum(dim=1).squeeze()
res = value[:-1] - value[1:]
res = res.to(torch.float16)
return res
hist_equiv = torch_histc_equivalent(tensor, hbins, hmin, hmax)
print(f"{hist_equiv=}")
print(f"delta={(hist_equiv - hist).to(int)}")
hist_equiv=tensor([ 128., 128., 256., 256., 256., 256., 512., 512., 1024.,
14336., 14336., 1024., 512., 512., 256., 256., 256., 256.,
128., 129.], dtype=torch.float16)
delta=tensor([ 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 3, 9112, 1856, -4,
-2, 0, -1, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1])
sum of differences 10984.0 with dtype=torch.float16.
This is not really satisfactory. Let’s check with float32.
hist32 = torch.histc(tensor.to(torch.float32), hbins, hmin, hmax)
hist32_equiv = torch_histc_equivalent(tensor.to(torch.float32), hbins, hmin, hmax)
diff32 = hist32_equiv - hist32
print(f"{diff32.abs().sum()} are misplaced: {diff32=}.")
10.0 are misplaced: diff32=tensor([ 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 4., -4., 0., 0., 0.,
0., 0., 0., 0., 0., -1.]).
Is histc an increasing function?¶
histc_index = torch.empty(tensor.shape, dtype=torch.float64)
buffer = torch.empty((1,), dtype=tensor.dtype)
for i in range(tensor.shape[0]):
buffer[0] = tensor[i]
histc_value = torch.histc(buffer, hbins, hmin, hmax)
histc_index[i] = (
histc_value.argmax() if histc_value.max().item() > 0 else histc_index.max()
)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1)
ax.plot(list(range(tensor.shape[0])), histc_index.tolist(), "-", label="histc_index")
ax.legend()
fig.savefig("plot_histc_index.png")
ax
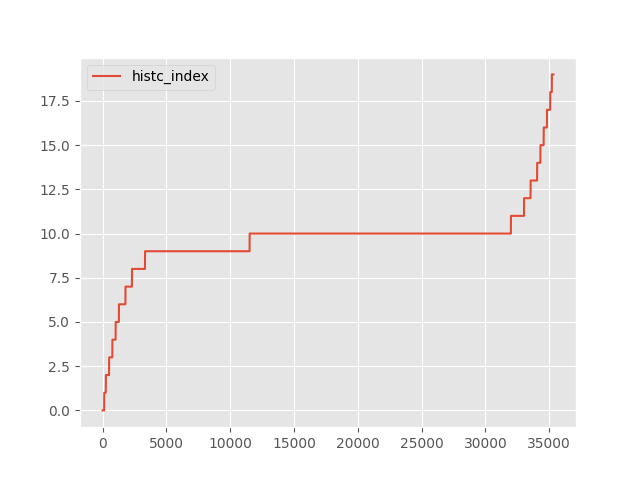
It seems growing. Let’s check.
diff = histc_index[1:] - histc_index[:-1]
print(f"min={diff.min()}, max={diff.max()}")
min=nan, max=nan
It is so we can find threshold working with the implementation we made.
Better thresholds¶
def tune_threshold_histc(
dtype: torch.dtype, hbin: int, hmin: float, hmax: float
) -> torch.Tensor:
possible_values = create_input(dtype, hmin, hmax)
buffer = torch.empty((1,), dtype=tensor.dtype)
previous_index = None
thresholds = []
for i in range(tensor.shape[0]):
buffer[0] = tensor[i]
histc_value = torch.histc(buffer, hbins, hmin, hmax)
if histc_value.max().item() > 0:
index = histc_value.argmax()
if previous_index is None or index != previous_index:
previous_index = index
thresholds.append(possible_values[i])
thresholds.append(
torch.nextafter(torch.tensor(hmax, dtype=dtype), torch.tensor(torch.inf, dtype=dtype))
)
return torch.tensor(thresholds, dtype=tensor.dtype)
thresholds = tune_threshold_histc(torch.float16, hbins, hmin, hmax)
print(f"shape={thresholds.shape}: {thresholds=}")
shape=torch.Size([21]): thresholds=tensor([-4.9961e+00, -4.5000e+00, -4.0000e+00, -3.5000e+00, -3.0000e+00,
-2.5000e+00, -2.0000e+00, -1.5010e+00, -1.0010e+00, -5.0195e-01,
-1.9531e-03, 4.9805e-01, 9.9805e-01, 1.4980e+00, 1.9980e+00,
2.4980e+00, 2.9980e+00, 3.4961e+00, 3.9961e+00, 4.4961e+00,
5.0039e+00], dtype=torch.float16)
Let’s check it is working.
hist_equiv = torch_histc_equivalent(tensor, hbins, hmin, hmax, thresholds=thresholds)
print(f"{hist_equiv=}")
print(f"delta={(hist_equiv - hist).to(int)}")
diff = torch.abs(hist_equiv - hist).sum()
print(f"sum of differences {diff} with {dtype=}.")
hist_equiv=tensor([ 127., 128., 256., 256., 256., 256., 511., 512., 1021.,
8192., 20480., 1028., 514., 512., 257., 256., 255., 256.,
129., 130.], dtype=torch.float16)
delta=tensor([ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2968, 8000, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
sum of differences 10968.0 with dtype=torch.float16.
That’s not really working. Let’s do another verification. We first start again by comparing the number of differences between histograms for the the whole tensor.
histc_value = torch.histc(tensor, hbins, hmin, hmax)
histc_equiv = torch_histc_equivalent(tensor, hbins, hmin, hmax, thresholds=thresholds)
diff = (histc_value - histc_equiv).abs()
print(f"with {tensor.shape[0]} elements, there {diff.sum()} differences.")
with 35329 elements, there 10968.0 differences.
We now take the elements with an even position.
histc_value = torch.histc(tensor[::2], hbins, hmin, hmax)
histc_equiv = torch_histc_equivalent(tensor[::2], hbins, hmin, hmax, thresholds=thresholds)
diff = (histc_value - histc_equiv).abs()
print(
f"with {tensor[::2].shape[0]} elements at even position, there {diff.sum()} differences."
)
with 17665 elements at even position, there 6.0 differences.
We now take the elements with an odd position.
histc_value = torch.histc(tensor[1::2], hbins, hmin, hmax)
histc_equiv = torch_histc_equivalent(tensor[1::2], hbins, hmin, hmax, thresholds=thresholds)
diff = (histc_value - histc_equiv).abs()
print(
f"with {tensor[1::2].shape[0]} elements at odd position, there {diff.sum()} differences."
)
with 17664 elements at odd position, there 6.0 differences.
This does not add up. Let’s prove now torch.histc() is really confusing.
The following sum should be null but it is not.
diff = torch.histc(tensor, hbins, hmin, hmax) - (
torch.histc(tensor[::2], hbins, hmin, hmax) + torch.histc(tensor[1::2], hbins, hmin, hmax)
)
print(f"torch.histc: {tensor.dtype=}, number of differences: {diff.abs().sum()}: {diff}")
torch.histc: tensor.dtype=torch.float16, number of differences: 10968.0: tensor([ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.,
-2968., -8000., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.,
0., 0.], dtype=torch.float16)
This does not add up. Our implementation is more reliable.
torch_histc_equivalent: tensor.dtype=torch.float16, number of differences: 0.0: tensor([0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
dtype=torch.float16)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.407 seconds)
Related examples