Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Reproducible Parallelized Reduction is difficult¶
A reduction is a frequent operation with neural networks. It appears in layer normalization,
softmax… Because of the float precision, the result of the computation
changes based on the order of the elements. The following examples show the variation
based on different hypothesis on the vector distribution.
We consider a vector .
It computes the average:
Or the normalization of the vector:
With ,
.
Methodology¶
Permutation should not change the average.
We draw 128 random permutations of X. The average or mean should not change. And the normalized vector should have the same values. In the first case, we compute the difference between the highest and the lowest values obtained for the average. In the second case, we look for the maximum difference between the original normalized vector and the permuted one, both sorted.
The computation code¶
import itertools
from tqdm import tqdm
import numpy as np
import pandas
DATA = []
def str_dtype(dtype):
"""Displays numpy dtype in a nicer way."""
if dtype == np.float64:
return "fp64"
if dtype == np.float32:
return "fp32"
if dtype == np.float16:
return "fp16"
raise ValueError(f"Unexpected value {dtype}")
def layer_norm(a, eps=1e-6):
"""
Normalized the vector a.
The computation is done in float32 or float64.
"""
ctype = np.float32 if a.dtype == np.float16 else a.dtype
a32 = a.astype(ctype)
m = a32.mean(axis=-1, keepdims=True)
c = a32 - m
va = np.sqrt((c * c).mean(axis=-1, keepdims=True))
va += eps
return (c / va).astype(a.dtype)
def compute(values, fct):
"""
Compare the results of function ``fct`` on a sample.
Loops over multiple sizes, dtypes. Tries 128 times.
"""
def make_value(base, value):
if value.size > 1:
return np.abs(np.sort(base) - np.sort(value)).max()
return value
sizes = [2, 4, 8, 16, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192]
dtypes = [np.float64, np.float32, np.float16]
N = list(range(128))
exps = list(itertools.product(sizes, dtypes, N))
data = []
ech = None
for size, dtype, n in tqdm(exps):
if n == 0:
ech = values[:size].astype(dtype)
base = fct(ech)
assert base.dtype == ech.dtype
obs = dict(
n=n, size=size, dtype=str_dtype(ech.dtype), value=make_value(base, fct(ech))
)
data.append(obs)
if n == 1:
new_ech = np.sort(ech)
elif n == 2:
new_ech = np.sort(ech)[::-1]
else:
new_ech = np.random.permutation(ech)
assert new_ech.dtype == ech.dtype
assert new_ech.shape == ech.shape
obs = dict(
n=n + 1,
size=size,
dtype=str_dtype(new_ech.dtype),
value=make_value(base, fct(new_ech)),
)
data.append(obs)
df = pandas.DataFrame(data)
agg = df.drop("n", axis=1).groupby(["dtype", "size"], as_index=False).agg(["min", "max"])
agg["value", "delta"] = agg["value", "max"] - agg["value", "min"]
piv = agg.pivot(index="size", columns="dtype", values=("value", "delta"))
return piv
Normal Law¶
Let’s see what it returns an on random sample following a normal law. First the average.
0%| | 0/3456 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 3028/3456 [00:00<00:00, 30243.33it/s]
100%|██████████| 3456/3456 [00:00<00:00, 22862.51it/s]
dtype fp16 fp32 fp64 name
size
2 0.0 0.000000e+00 0.000000e+00 normal
4 0.0 7.450581e-09 4.163336e-17 normal
8 0.0 5.960464e-08 1.110223e-16 normal
16 0.0 4.470348e-08 8.326673e-17 normal
512 0.0 3.539026e-08 3.469447e-17 normal
1024 0.0 2.887100e-08 1.110223e-16 normal
2048 0.0 2.980232e-08 2.341877e-17 normal
4096 0.0 1.676381e-08 5.551115e-17 normal
8192 0.0 1.769513e-08 5.551115e-17 normal
Then the layer normalization.
0%| | 0/3456 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 2326/3456 [00:00<00:00, 23244.12it/s]
100%|██████████| 3456/3456 [00:00<00:00, 6478.01it/s]
dtype fp16 fp32 fp64 name
size
2 0.0 0.000000e+00 0.000000e+00 normal
4 0.0 1.192093e-07 2.220446e-16 normal
8 0.0 1.788139e-07 4.440892e-16 normal
16 0.0 2.384186e-07 2.220446e-16 normal
512 0.0 2.384186e-07 4.440892e-16 normal
1024 0.0 2.384186e-07 8.881784e-16 normal
2048 0.0 2.384186e-07 8.881784e-16 normal
4096 0.0 4.768372e-07 8.881784e-16 normal
8192 0.0 4.768372e-07 8.881784e-16 normal
Fixed values¶
We try a fixed vector with one very high value and all the others are small.
0%| | 0/3456 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
81%|████████▏ | 2809/3456 [00:00<00:00, 28058.52it/s]
100%|██████████| 3456/3456 [00:00<00:00, 19030.85it/s]
dtype fp16 fp32 fp64 name
size
2 0.0 0.000000e+00 0.000000e+00 fixed
4 0.0 0.000000e+00 3.552714e-15 fixed
8 0.0 0.000000e+00 0.000000e+00 fixed
16 0.0 0.000000e+00 0.000000e+00 fixed
512 0.0 1.788139e-07 4.440892e-16 fixed
1024 0.0 2.384186e-07 5.551115e-16 fixed
2048 0.0 4.768372e-07 4.440892e-16 fixed
4096 0.0 2.980232e-07 9.992007e-16 fixed
8192 0.0 2.980232e-07 9.992007e-16 fixed
And the normalized vector.
0%| | 0/3456 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 2309/3456 [00:00<00:00, 23065.00it/s]
100%|██████████| 3456/3456 [00:00<00:00, 11237.32it/s]
dtype fp16 fp32 fp64 name
size
2 0.0 0.000000 0.000000e+00 fixed
4 0.0 0.000000 2.220446e-16 fixed
8 0.0 0.000000 0.000000e+00 fixed
16 0.0 0.000000 0.000000e+00 fixed
512 0.0 0.000003 1.776357e-15 fixed
1024 0.0 0.000002 1.776357e-15 fixed
2048 0.0 0.000004 7.105427e-15 fixed
4096 0.0 0.000002 1.776357e-15 fixed
8192 0.0 0.000002 1.776357e-15 fixed
Pareto Distribution¶
A law with a long tail.
[0.05300402 0.07376355 0.39489129 ... 0.63390079 2.75062029 0.02519434]
0%| | 0/3456 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 3050/3456 [00:00<00:00, 30478.74it/s]
100%|██████████| 3456/3456 [00:00<00:00, 23161.66it/s]
dtype fp16 fp32 fp64 name
size
2 0.0 0.000000e+00 0.000000e+00 normal
4 0.0 1.192093e-07 0.000000e+00 normal
8 0.0 2.384186e-07 2.220446e-16 normal
16 0.0 2.384186e-07 4.440892e-16 normal
512 0.0 7.152557e-07 8.881784e-16 normal
1024 0.0 9.536743e-07 1.776357e-15 normal
2048 0.0 9.536743e-07 1.776357e-15 normal
4096 0.0 9.536743e-07 3.552714e-15 normal
8192 0.0 1.907349e-06 3.552714e-15 normal
And the normalized vector.
0%| | 0/3456 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 2217/3456 [00:00<00:00, 22135.77it/s]
100%|██████████| 3456/3456 [00:00<00:00, 7267.78it/s]
dtype fp16 fp32 fp64 name
size
2 0.000000 0.000000e+00 0.000000e+00 pareto
4 0.000000 1.788139e-07 0.000000e+00 pareto
8 0.000000 2.384186e-07 2.220446e-16 pareto
16 0.000000 2.384186e-07 4.440892e-16 pareto
512 0.000000 1.907349e-06 3.552714e-15 pareto
1024 0.000000 5.722046e-06 7.105427e-15 pareto
2048 0.000004 3.814697e-06 7.105427e-15 pareto
4096 0.000061 7.629395e-06 2.131628e-14 pareto
8192 0.000061 7.629395e-06 2.131628e-14 pareto
Summary¶
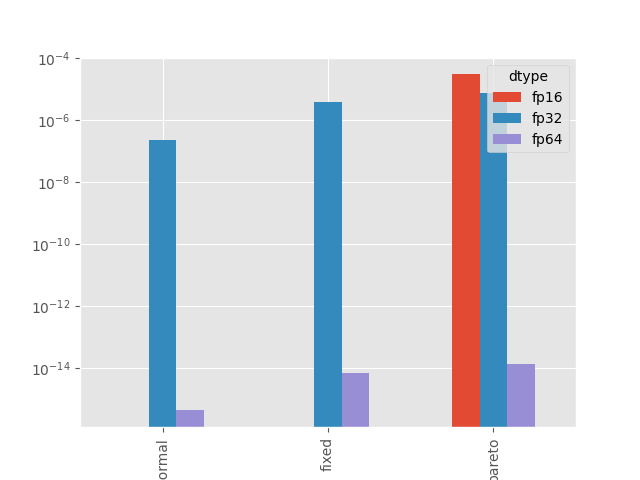
We consider the maximum difference obtained for any sample size.
df = pandas.DataFrame(DATA).set_index("name")
print(df)
dtype fp16 fp32 fp64
name
normal 0.000000 4.768372e-07 8.881784e-16
fixed 0.000000 3.814697e-06 7.105427e-15
pareto 0.000061 7.629395e-06 2.131628e-14
Visually.
ax = df.plot.bar(logy=True)
ax.set_xticklabels(ax.get_xticklabels(), rotation=45)
fig = ax.get_figure()
fig.savefig("plot_parallelized_reduction.png")
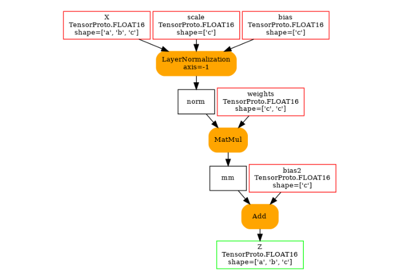
In a deep neural network¶
Some of the vector have 500 values, 16x32x1024x1024. A layer normalization does 16x32x1024 ~ 2M reductions, over 20 layers. When a deep neural network is computed with a different code doing a different parallelization (GPU/CPU for example), the order of the reduction may change and therefore, some errors will appear and propagate.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.279 seconds)
Related examples
LayerNormalization implementation cannot be exchanged