Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
How float format has an impact on speed computation#
An example with Conv. The floats followed the IEEE standard Single-precision floating-point format. The number is interprated in a different whether the exponent is null or not. When it is null, it is called a denormalized number or subnormal number. Let’s see their impact on the computation time through the operator Conv.
Create one model#
import struct
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pandas import DataFrame
from tqdm import tqdm
import numpy
from onnx import TensorProto
from onnx.helper import (
make_model,
make_node,
make_graph,
make_tensor_value_info,
make_opsetid,
)
from onnx.checker import check_model
from onnx.numpy_helper import to_array, from_array
from onnxruntime import (
InferenceSession,
get_available_providers,
OrtValue,
SessionOptions,
GraphOptimizationLevel,
)
from onnx_array_api.plotting.text_plot import onnx_simple_text_plot
from onnx_extended.ext_test_case import measure_time, unit_test_going
from onnx_extended.reference import CReferenceEvaluator
try:
import torch
except ImportError:
# no torch is available
print("torch is not available")
torch = None
DIM = 64 if unit_test_going() else 256
def _denorm(x):
i = int.from_bytes(struct.pack("<f", numpy.float32(x)), "little")
i &= 0x807FFFFF
return numpy.uint32(i).view(numpy.float32)
denorm = numpy.vectorize(_denorm)
def create_model():
X = make_tensor_value_info("X", TensorProto.FLOAT, [1, DIM, 14, 14])
Y = make_tensor_value_info("Y", TensorProto.FLOAT, [None, None, None, None])
B = from_array(numpy.zeros([DIM], dtype=numpy.float32), name="B")
w = numpy.random.randn(DIM, DIM, 3, 3).astype(numpy.float32)
# let's randomly denormalize some number
mask = (numpy.random.randint(2, size=w.shape) % 2).astype(numpy.float32)
d = denorm(w)
w = w * mask - (mask - 1) * d
W = from_array(w, name="W")
node1 = make_node(
"Conv", ["X", "W", "B"], ["Y"], kernel_shape=[3, 3], pads=[1, 1, 1, 1]
)
graph = make_graph([node1], "lr", [X], [Y], [W, B])
onnx_model = make_model(graph, opset_imports=[make_opsetid("", 18)], ir_version=8)
check_model(onnx_model)
return onnx_model
onx = create_model()
onnx_file = "plot_op_conv_denorm.onnx"
with open(onnx_file, "wb") as f:
f.write(onx.SerializeToString())
The model looks like:
print(onnx_simple_text_plot(onx))
onnx_model = onnx_file
input_shape = (1, DIM, 14, 14)
opset: domain='' version=18
input: name='X' type=dtype('float32') shape=[1, 256, 14, 14]
init: name='W' type=dtype('float32') shape=(256, 256, 3, 3)
init: name='B' type=dtype('float32') shape=(256,)
Conv(X, W, B, kernel_shape=[3,3], pads=[1,1,1,1]) -> Y
output: name='Y' type=dtype('float32') shape=['', '', '', '']
CReferenceEvaluator and InferenceSession#
Let’s first compare the outputs are the same.
sess_options = SessionOptions()
sess_options.graph_optimization_level = GraphOptimizationLevel.ORT_DISABLE_ALL
sess1 = CReferenceEvaluator(onnx_model)
sess2 = InferenceSession(onnx_model, sess_options, providers=["CPUExecutionProvider"])
X = numpy.ones(input_shape, dtype=numpy.float32)
expected = sess1.run(None, {"X": X})[0]
got = sess2.run(None, {"X": X})[0]
diff = numpy.abs(expected - got).max()
print(f"difference: {diff}")
difference: 3.337860107421875e-05
Everything works fine.
Time measurement#
CReferenceEvaluator: 0.13534609999996974s
InferenceSession: 0.10375600000002123s
Plotting#
Let’s modify the the weight of the model and multiply everything by a scalar. Let’s choose an random input.
has_cuda = "CUDAExecutionProvider" in get_available_providers()
X = numpy.random.random(X.shape).astype(X.dtype)
def modify(onx, scale):
t = to_array(onx.graph.initializer[0])
b = to_array(onx.graph.initializer[1]).copy()
t = (t * scale).astype(numpy.float32)
graph = make_graph(
onx.graph.node,
onx.graph.name,
onx.graph.input,
onx.graph.output,
[from_array(t, name=onx.graph.initializer[0].name), onx.graph.initializer[1]],
)
model = make_model(graph, opset_imports=onx.opset_import, ir_version=onx.ir_version)
return t, b, model
scales = [2**p for p in range(0, 31, 2)]
data = []
feeds = {"X": X}
expected = sess2.run(None, feeds)[0]
if torch is not None:
tx = torch.from_numpy(X)
sess_options0 = SessionOptions()
sess_options0.graph_optimization_level = GraphOptimizationLevel.ORT_DISABLE_ALL
sess_options0.add_session_config_entry("session.set_denormal_as_zero", "1")
for scale in tqdm(scales):
w, b, new_onx = modify(onx, scale)
n_denorm = (w == denorm(w)).astype(numpy.int32).sum() / w.size
# sess1 = CReferenceEvaluator(new_onx)
sess2 = InferenceSession(
new_onx.SerializeToString(), sess_options, providers=["CPUExecutionProvider"]
)
sess3 = InferenceSession(
new_onx.SerializeToString(), providers=["CPUExecutionProvider"]
)
sess4 = InferenceSession(
new_onx.SerializeToString(), sess_options0, providers=["CPUExecutionProvider"]
)
# sess1.run(None, feeds)
got = sess2.run(None, feeds)[0]
diff = numpy.abs(got / scale - expected).max()
sess3.run(None, feeds)
got0 = sess4.run(None, feeds)[0]
diff0 = numpy.abs(got0 / scale - expected).max()
# t1 = measure_time(lambda: sess1.run(None, feeds), repeat=2, number=5)
t2 = measure_time(lambda: sess2.run(None, feeds), repeat=2, number=5)
t3 = measure_time(lambda: sess3.run(None, feeds), repeat=2, number=5)
t4 = measure_time(lambda: sess4.run(None, feeds), repeat=2, number=5)
obs = dict(
scale=scale,
ort=t2["average"],
diff=diff,
diff0=diff0,
ort0=t4["average"],
n_denorm=n_denorm,
)
# obs["ref"]=t1["average"]
obs["ort-opt"] = t3["average"]
if torch is not None:
tw = torch.from_numpy(w)
tb = torch.from_numpy(b)
torch.nn.functional.conv2d(tx, tw, tb, padding=1)
t3 = measure_time(
lambda: torch.nn.functional.conv2d(tx, tw, tb, padding=1),
repeat=2,
number=5,
)
obs["torch"] = t3["average"]
if has_cuda:
sess2 = InferenceSession(
new_onx.SerializeToString(),
sess_options,
providers=["CUDAExecutionProvider"],
)
sess3 = InferenceSession(
new_onx.SerializeToString(), providers=["CUDAExecutionProvider"]
)
x_ortvalue = OrtValue.ortvalue_from_numpy(X, "cuda", 0)
cuda_feeds = {"X": x_ortvalue}
sess2.run_with_ort_values(None, cuda_feeds)
sess3.run_with_ort_values(None, cuda_feeds)
t2 = measure_time(lambda: sess2.run(None, cuda_feeds), repeat=2, number=5)
t3 = measure_time(lambda: sess3.run(None, cuda_feeds), repeat=2, number=5)
obs["ort-cuda"] = t2["average"]
obs["ort-cuda-opt"] = t2["average"]
data.append(obs)
if unit_test_going() and len(data) >= 2:
break
df = DataFrame(data)
df
0%| | 0/16 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
6%|▋ | 1/16 [00:19<04:56, 19.80s/it]
12%|█▎ | 2/16 [00:24<02:36, 11.16s/it]
19%|█▉ | 3/16 [00:28<01:38, 7.59s/it]
25%|██▌ | 4/16 [00:30<01:04, 5.38s/it]
31%|███▏ | 5/16 [00:31<00:44, 4.01s/it]
38%|███▊ | 6/16 [00:33<00:31, 3.16s/it]
44%|████▍ | 7/16 [00:34<00:23, 2.62s/it]
50%|█████ | 8/16 [00:36<00:18, 2.26s/it]
56%|█████▋ | 9/16 [00:37<00:14, 2.04s/it]
62%|██████▎ | 10/16 [00:39<00:11, 1.92s/it]
69%|██████▉ | 11/16 [00:41<00:08, 1.79s/it]
75%|███████▌ | 12/16 [00:42<00:06, 1.69s/it]
81%|████████▏ | 13/16 [00:43<00:04, 1.63s/it]
88%|████████▊ | 14/16 [00:45<00:03, 1.58s/it]
94%|█████████▍| 15/16 [00:46<00:01, 1.55s/it]
100%|██████████| 16/16 [00:48<00:00, 1.53s/it]
100%|██████████| 16/16 [00:48<00:00, 3.03s/it]
Finally.
dfp = df.drop(["diff", "diff0", "n_denorm"], axis=1).set_index("scale")
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 4))
dfp.plot(ax=ax[0], logx=True, logy=True, title="Comparison of Conv processing time")
df[["n_denorm"]].plot(
ax=ax[1], logx=True, logy=True, title="Ratio of denormalized numbers"
)
fig.tight_layout()
fig.savefig("plot_op_conv_denorm.png")
# plt.show()
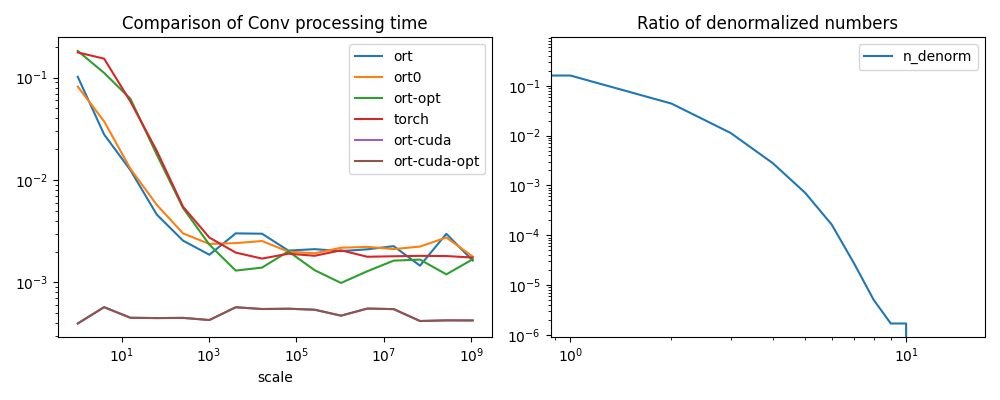
Conclusion#
Denormalized numbers should be avoided.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 54.197 seconds)