Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Predictable t-SNE#
t-SNE is not a transformer which can produce outputs for other inputs than the one used to train the transform. The proposed solution is train a predictor afterwards to try to use the results on some other inputs the model never saw.
t-SNE on MNIST#
Let’s reuse some part of the example of Manifold learning on handwritten digits: Locally Linear Embedding, Isomap.
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import offsetbox
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsRegressor
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from mlinsights.mlmodel import PredictableTSNE
digits = datasets.load_digits(n_class=6)
Xd = digits.data
yd = digits.target
imgs = digits.images
n_samples, n_features = Xd.shape
n_samples, n_features
(1083, 64)
Let’s split into train and test.
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test, imgs_train, imgs_test = train_test_split(Xd, yd, imgs)
tsne = TSNE(n_components=2, init="pca", random_state=0)
X_train_tsne = tsne.fit_transform(X_train, y_train)
X_train_tsne.shape
(812, 2)
def plot_embedding(Xp, y, imgs, title=None, figsize=(12, 4)):
x_min, x_max = numpy.min(Xp, 0), numpy.max(Xp, 0)
X = (Xp - x_min) / (x_max - x_min)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=figsize)
for i in range(X.shape[0]):
ax[0].text(
X[i, 0],
X[i, 1],
str(y[i]),
color=plt.cm.Set1(y[i] / 10.0),
fontdict={"weight": "bold", "size": 9},
)
if hasattr(offsetbox, "AnnotationBbox"):
# only print thumbnails with matplotlib > 1.0
shown_images = numpy.array([[1.0, 1.0]]) # just something big
for i in range(X.shape[0]):
dist = numpy.sum((X[i] - shown_images) ** 2, 1)
if numpy.min(dist) < 4e-3:
# don't show points that are too close
continue
shown_images = numpy.r_[shown_images, [X[i]]]
imagebox = offsetbox.AnnotationBbox(
offsetbox.OffsetImage(imgs[i], cmap=plt.cm.gray_r), X[i]
)
ax[0].add_artist(imagebox)
ax[0].set_xticks([]), ax[0].set_yticks([])
ax[1].plot(Xp[:, 0], Xp[:, 1], ".")
if title is not None:
ax[0].set_title(title)
return ax
plot_embedding(X_train_tsne, y_train, imgs_train, "t-SNE embedding of the digits")
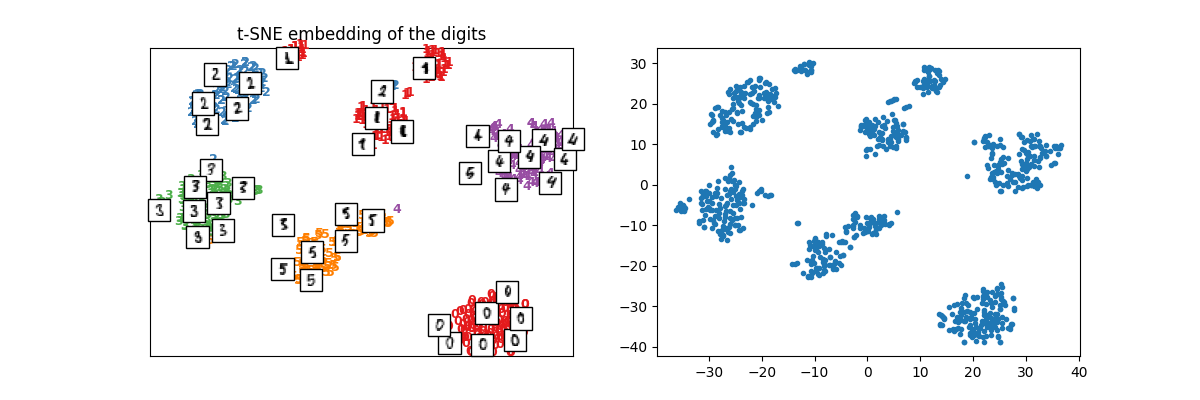
array([<Axes: title={'center': 't-SNE embedding of the digits'}>,
<Axes: >], dtype=object)
Repeatable t-SNE#
We use class PredictableTSNE but it works for other trainable transform too.
ptsne = PredictableTSNE()
ptsne.fit(X_train, y_train)
~/install/scikit-learn/sklearn/neural_network/_multilayer_perceptron.py:691: ConvergenceWarning: Stochastic Optimizer: Maximum iterations (200) reached and the optimization hasn't converged yet.
warnings.warn(
X_train_tsne2 = ptsne.transform(X_train)
plot_embedding(X_train_tsne2, y_train, imgs_train, "Predictable t-SNE of the digits")
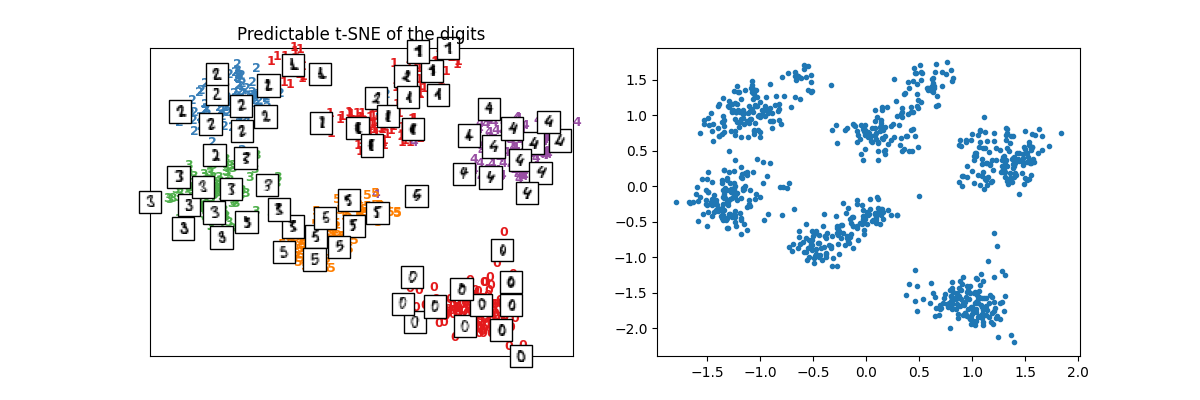
array([<Axes: title={'center': 'Predictable t-SNE of the digits'}>,
<Axes: >], dtype=object)
The difference now is that it can be applied on new data.
X_test_tsne2 = ptsne.transform(X_test)
plot_embedding(
X_test_tsne2, y_test, imgs_test, "Predictable t-SNE on new digits on test database"
)
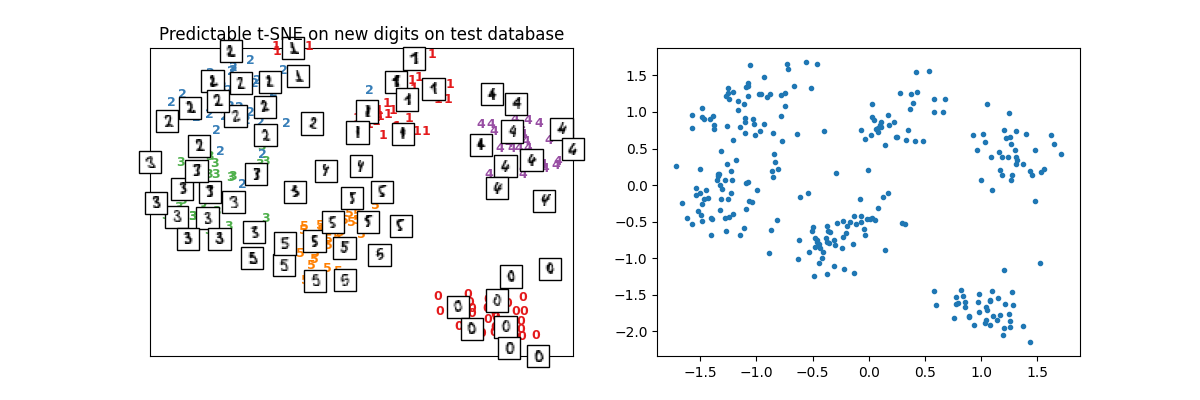
array([<Axes: title={'center': 'Predictable t-SNE on new digits on test database'}>,
<Axes: >], dtype=object)
By default, the output data is normalized to get comparable results over multiple tries such as the loss computed between the normalized output of t-SNE and their approximation.
0.015498107687307933
Repeatable t-SNE with another predictor#
# The predictor is a
# `MLPRegressor <https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.neural_network.MLPRegressor.html>`_.
ptsne.estimator_
Let’s replace it with a KNeighborsRegressor and a normalizer StandardScaler.
ptsne_knn = PredictableTSNE(
normalizer=StandardScaler(), estimator=KNeighborsRegressor()
)
ptsne_knn.fit(X_train, y_train)
X_train_tsne2 = ptsne_knn.transform(X_train)
plot_embedding(
X_train_tsne2,
y_train,
imgs_train,
"Predictable t-SNE of the digits\nStandardScaler+KNeighborsRegressor",
)
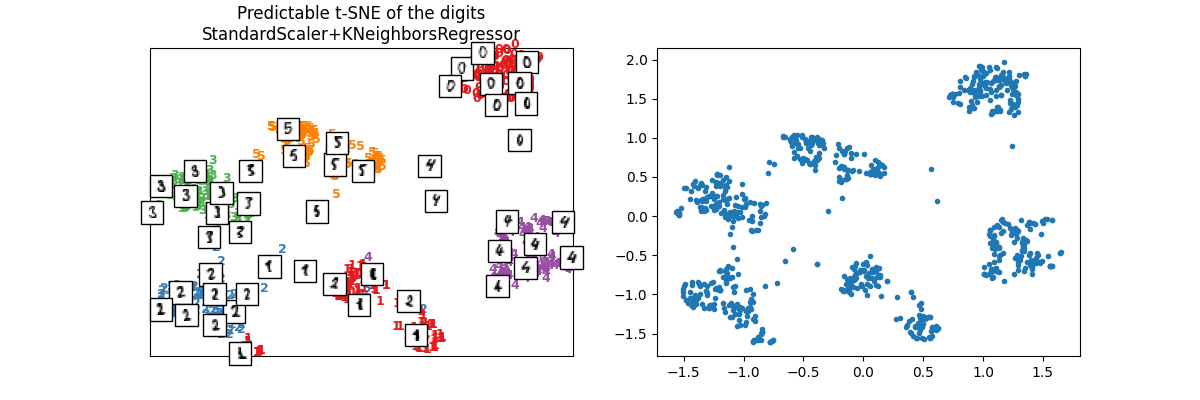
array([<Axes: title={'center': 'Predictable t-SNE of the digits\nStandardScaler+KNeighborsRegressor'}>,
<Axes: >], dtype=object)
X_test_tsne2 = ptsne_knn.transform(X_test)
plot_embedding(
X_test_tsne2,
y_test,
imgs_test,
"Predictable t-SNE on new digits\nStandardScaler+KNeighborsRegressor",
)
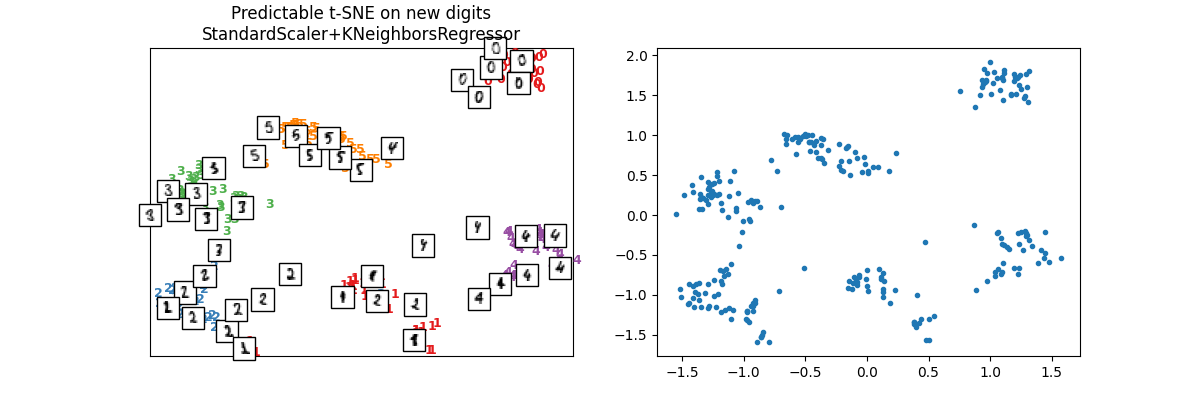
array([<Axes: title={'center': 'Predictable t-SNE on new digits\nStandardScaler+KNeighborsRegressor'}>,
<Axes: >], dtype=object)
The model seems to work better as the loss is better but as it is evaluated on the training dataset, it is just a way to check it is not too big.
0.0036627657
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 12.744 seconds)