Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Piecewise classification with scikit-learn predictors#
Piecewise regression is easier to understand but the concept can be extended to classification. That’s what this notebook explores.
Iris dataset and first logistic regression#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn
import numpy
import pandas
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.dummy import DummyClassifier
from sklearn.preprocessing import KBinsDiscretizer
from sklearn.metrics import auc, roc_curve
from mlinsights.mlmodel import PiecewiseClassifier
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, :2] # we only take the first two features.
Y = iris.target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y)
def graph(X, Y, model):
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 0.5, X[:, 0].max() + 0.5
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 0.5, X[:, 1].max() + 0.5
h = 0.02 # step size in the mesh
xx, yy = numpy.meshgrid(
numpy.arange(x_min, x_max, h), numpy.arange(y_min, y_max, h)
)
Z = model.predict(numpy.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
# Put the result into a color plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(4, 3))
ax.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Paired)
# Plot also the training points
ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=Y, edgecolors="k", cmap=plt.cm.Paired)
ax.set_xlabel("Sepal length")
ax.set_ylabel("Sepal width")
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
return ax
logreg = LogisticRegression()
logreg.fit(X_train, y_train)
ax = graph(X_test, y_test, logreg)
ax.set_title("LogisticRegression")
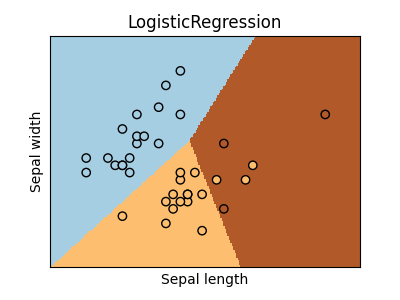
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'LogisticRegression')
Piecewise classication#
dummy = DummyClassifier(strategy="most_frequent")
piece4 = PiecewiseClassifier(KBinsDiscretizer(n_bins=2), estimator=dummy, verbose=True)
piece4.fit(X_train, y_train)
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Using backend SequentialBackend with 1 concurrent workers.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 4 out of 4 | elapsed: 0.0s finished
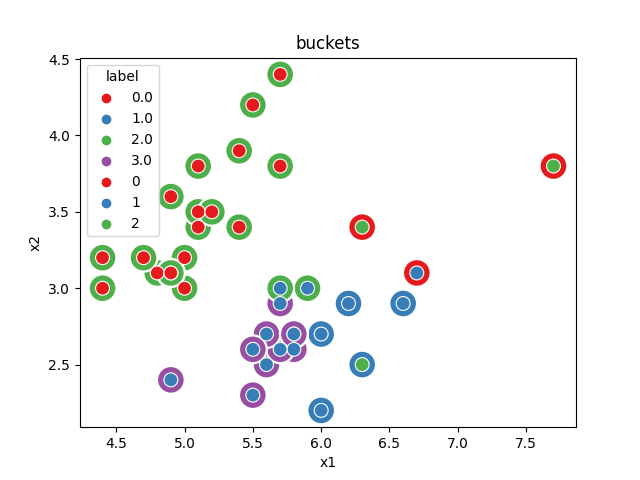
We look into the bucket given to each point.
~/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/seaborn/_oldcore.py:1498: FutureWarning: is_categorical_dtype is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Use isinstance(dtype, CategoricalDtype) instead
if pd.api.types.is_categorical_dtype(vector):
~/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/seaborn/_oldcore.py:1498: FutureWarning: is_categorical_dtype is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Use isinstance(dtype, CategoricalDtype) instead
if pd.api.types.is_categorical_dtype(vector):
~/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/seaborn/_oldcore.py:1498: FutureWarning: is_categorical_dtype is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Use isinstance(dtype, CategoricalDtype) instead
if pd.api.types.is_categorical_dtype(vector):
~/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/seaborn/_oldcore.py:1498: FutureWarning: is_categorical_dtype is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Use isinstance(dtype, CategoricalDtype) instead
if pd.api.types.is_categorical_dtype(vector):
~/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/seaborn/_oldcore.py:1498: FutureWarning: is_categorical_dtype is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Use isinstance(dtype, CategoricalDtype) instead
if pd.api.types.is_categorical_dtype(vector):
~/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/seaborn/_oldcore.py:1498: FutureWarning: is_categorical_dtype is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Use isinstance(dtype, CategoricalDtype) instead
if pd.api.types.is_categorical_dtype(vector):
~/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/seaborn/_oldcore.py:1498: FutureWarning: is_categorical_dtype is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Use isinstance(dtype, CategoricalDtype) instead
if pd.api.types.is_categorical_dtype(vector):
~/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/seaborn/_oldcore.py:1498: FutureWarning: is_categorical_dtype is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Use isinstance(dtype, CategoricalDtype) instead
if pd.api.types.is_categorical_dtype(vector):
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'buckets')
We see there are four buckets. Two buckets only contains one label. The dummy classifier maps every bucket to the most frequent class in the bucket.
ax = graph(X_test, y_test, piece4)
ax.set_title("Piecewise Classification\n4 buckets")
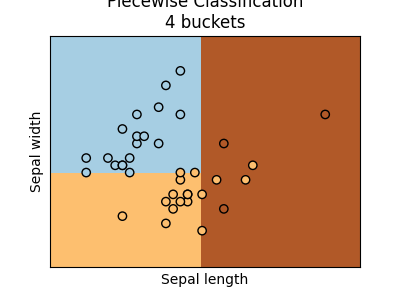
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Piecewise Classification\n4 buckets')
We can increase the number of buckets.
dummy = DummyClassifier(strategy="most_frequent")
piece9 = PiecewiseClassifier(KBinsDiscretizer(n_bins=3), estimator=dummy, verbose=True)
piece9.fit(X_train, y_train)
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Using backend SequentialBackend with 1 concurrent workers.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 9 out of 9 | elapsed: 0.0s finished
ax = graph(X_test, y_test, piece9)
ax.set_title("Piecewise Classification\n9 buckets")
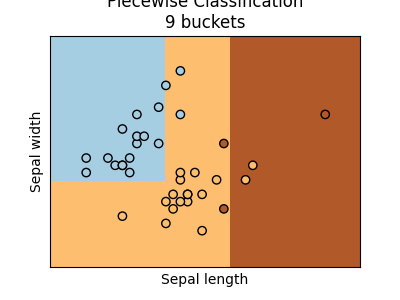
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Piecewise Classification\n9 buckets')
Let’s compute the ROC curve.
def plot_roc_curve(models, X, y):
if not isinstance(models, dict):
return plot_roc_curve({models.__class__.__name__: models}, X, y)
ax = None
colors = "bgrcmyk"
for ic, (name, model) in enumerate(models.items()):
fpr, tpr, roc_auc = dict(), dict(), dict()
nb = len(model.classes_)
y_score = model.predict_proba(X)
for i in range(nb):
c = model.classes_[i]
fpr[i], tpr[i], _ = roc_curve(y_test == c, y_score[:, i])
roc_auc[i] = auc(fpr[i], tpr[i])
if ax is None:
lw = 2
_, ax = plt.subplots(1, nb, figsize=(4 * nb, 4))
for i in range(nb):
ax[i].plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color="navy", lw=lw, linestyle="--")
plotname = "".join(c for c in name if "A" <= c <= "Z" or "0" <= c <= "9")
for i in range(nb):
ax[i].plot(
fpr[i],
tpr[i],
color=colors[ic],
lw=lw,
label="%0.2f %s" % (roc_auc[i], plotname),
)
ax[i].set_title("class {}".format(model.classes_[i]))
for k in range(ax.shape[0]):
ax[k].legend()
return ax
plot_roc_curve({"LR": logreg, "P4": piece4, "P9": piece9}, X_test, y_test)
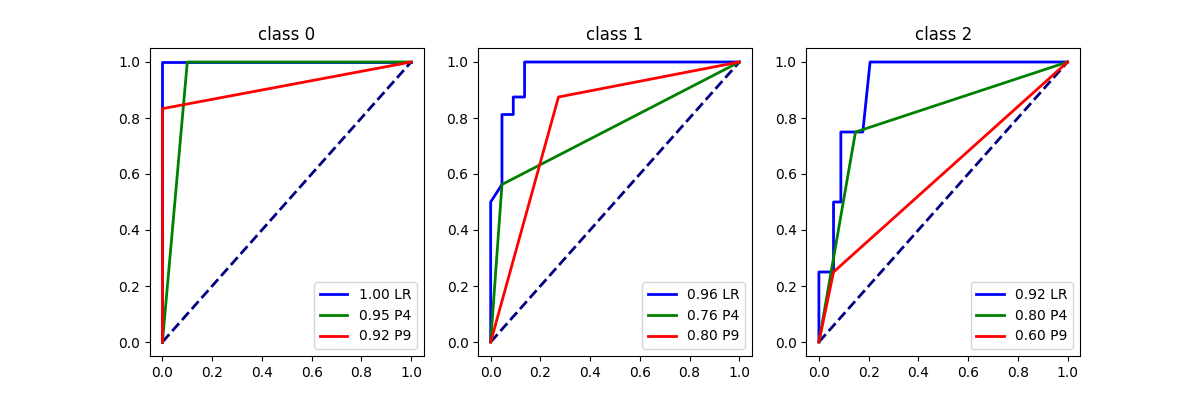
array([<Axes: title={'center': 'class 0'}>,
<Axes: title={'center': 'class 1'}>,
<Axes: title={'center': 'class 2'}>], dtype=object)
Let’s use the decision tree to create buckets.
dummy = DummyClassifier(strategy="most_frequent")
pieceT = PiecewiseClassifier("tree", estimator=dummy, verbose=True)
pieceT.fit(X_train, y_train)
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Using backend SequentialBackend with 1 concurrent workers.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 15 out of 15 | elapsed: 0.0s finished
ax = graph(X_test, y_test, pieceT)
ax.set_title("Piecewise Classification\n%d buckets (tree)" % len(pieceT.estimators_))
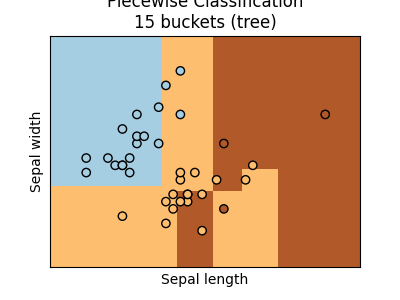
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Piecewise Classification\n15 buckets (tree)')
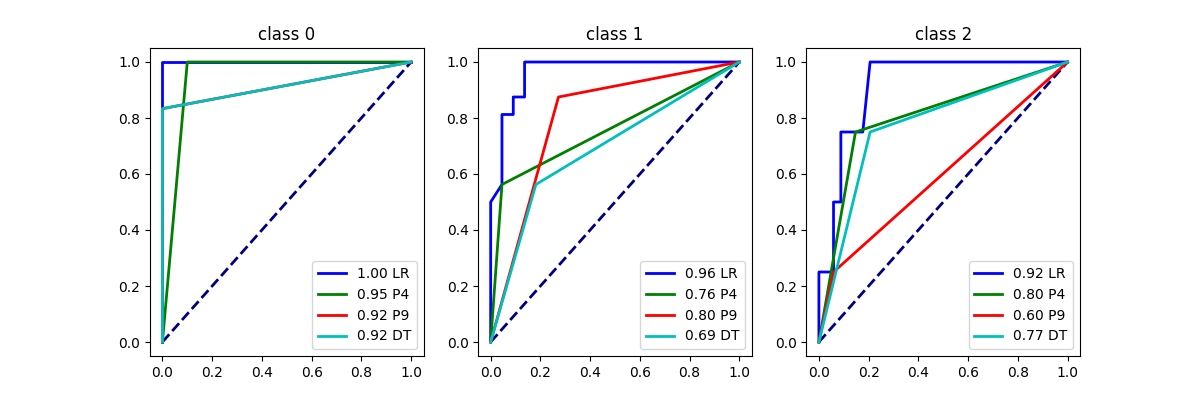
array([<Axes: title={'center': 'class 0'}>,
<Axes: title={'center': 'class 1'}>,
<Axes: title={'center': 'class 2'}>], dtype=object)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 5.798 seconds)