Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Measuring CPU performance¶
Processor caches must be taken into account when writing an algorithm, see Memory part 2: CPU caches from Ulrich Drepper.
Cache Performance¶
Code of benchmark_cache.
obs = []
step = 2**12
for i in tqdm(range(step, 2**20 + step, step)):
res = min(
[
benchmark_cache(i, False),
benchmark_cache(i, False),
benchmark_cache(i, False),
]
)
if res < 0:
# overflow
continue
obs.append(dict(size=i, perf=res))
df = DataFrame(obs)
mean = df.perf.mean()
lag = 32
for i in range(2, df.shape[0]):
df.loc[i, "smooth"] = df.loc[i - 8 : i + 8, "perf"].median()
if i > lag and i < df.shape[0] - lag:
df.loc[i, "delta"] = (
mean
+ df.loc[i : i + lag, "perf"].mean()
- df.loc[i - lag + 1 : i + 1, "perf"]
).mean()
0%| | 0/256 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
50%|████▉ | 127/256 [00:00<00:00, 1269.83it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 254/256 [00:00<00:00, 744.94it/s]
100%|██████████| 256/256 [00:00<00:00, 788.15it/s]
Cache size estimator¶
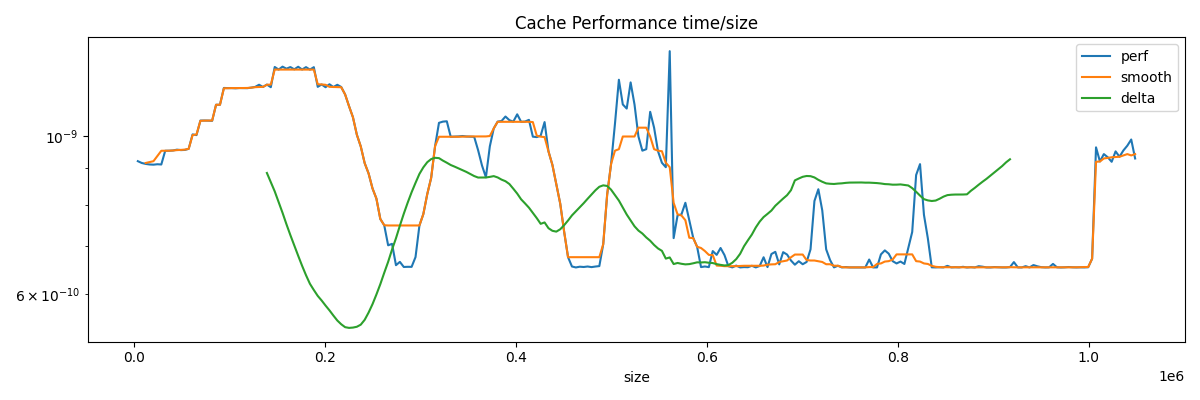
cache_size_index = int(df.delta.argmax())
cache_size = df.loc[cache_size_index, "size"] * 2
print(f"L2 cache size estimation is {cache_size / 2 ** 20:1.3f} Mb.")
L2 cache size estimation is 0.266 Mb.
Verification¶
try:
out, err = run_cmd("lscpu", wait=True)
print("\n".join(_ for _ in out.split("\n") if "cache:" in _))
except Exception as e:
print(f"failed due to {e}")
df = df.set_index("size")
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(12, 4))
df.plot(ax=ax, title="Cache Performance time/size", logy=True)
fig.tight_layout()
fig.savefig("plot_benchmark_cpu_array.png")
L1d cache: 480 KiB (10 instances)
L1i cache: 320 KiB (10 instances)
L2 cache: 12.5 MiB (10 instances)
L3 cache: 24 MiB (1 instance)
TreeEnsemble Performance¶
We simulate the computation of a TreeEnsemble
of 50 features, 100 trees and depth of 10
(so nodes.)
The code of benchmark_cache_tree
dfs = []
cols = []
drop = []
for n in tqdm(range(2 if unit_test_going() else 5)):
res = benchmark_cache_tree(
n_rows=2000,
n_features=50,
n_trees=100,
tree_size=1024,
max_depth=10,
search_step=64,
)
res = [[max(r.row, i), r.time] for i, r in enumerate(res)]
df = DataFrame(res)
df.columns = [f"i{n}", f"time{n}"]
dfs.append(df)
cols.append(df.columns[-1])
drop.append(df.columns[0])
df = concat(dfs, axis=1).reset_index(drop=True)
df["i"] = df["i0"]
df = df.drop(drop, axis=1)
df["time_avg"] = df[cols].mean(axis=1)
df["time_med"] = df[cols].median(axis=1)
df.head()
0%| | 0/5 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
20%|██ | 1/5 [00:00<00:01, 2.40it/s]
40%|████ | 2/5 [00:00<00:01, 2.48it/s]
60%|██████ | 3/5 [00:01<00:00, 2.50it/s]
80%|████████ | 4/5 [00:01<00:00, 2.50it/s]
100%|██████████| 5/5 [00:01<00:00, 2.52it/s]
100%|██████████| 5/5 [00:01<00:00, 2.50it/s]
Estimation¶
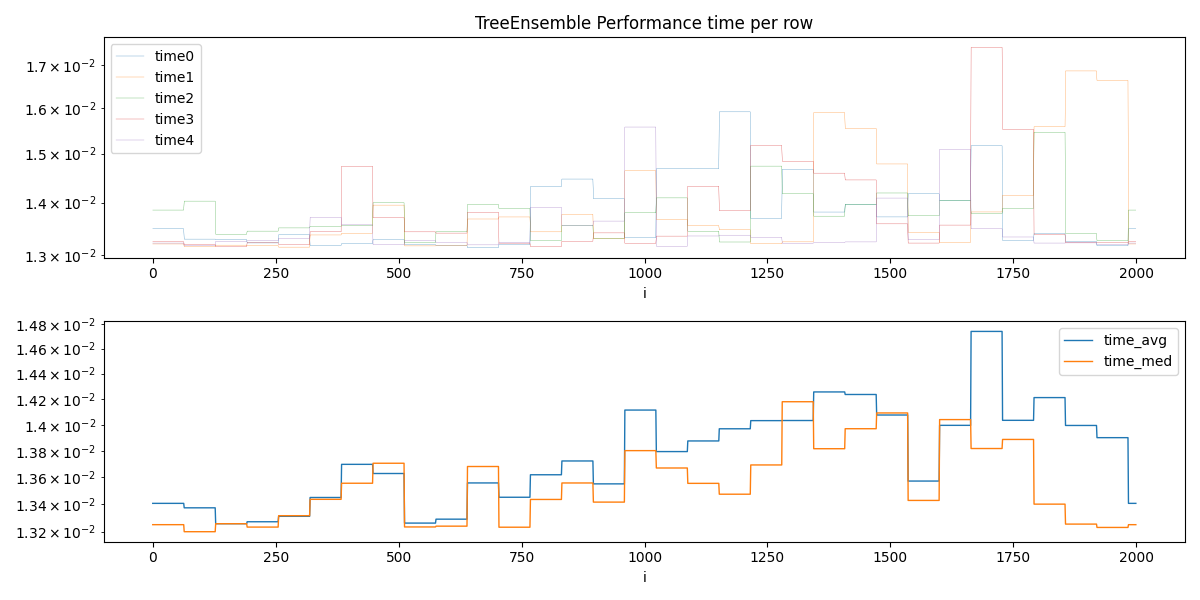
Optimal batch size is among:
i time_med time_avg
0 1664 0.012523 0.012530
1 256 0.012525 0.012540
2 1344 0.012532 0.012811
3 448 0.012532 0.012601
4 384 0.012534 0.012563
5 1024 0.012539 0.012536
6 896 0.012541 0.012561
7 1856 0.012545 0.012842
8 576 0.012545 0.012566
9 320 0.012545 0.013708
One possible estimation
Estimation: 957.8479130555965
Plots.
cols_time = ["time_avg", "time_med"]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(12, 6))
df.set_index("i").drop(cols_time, axis=1).plot(
ax=ax[0], title="TreeEnsemble Performance time per row", logy=True, linewidth=0.2
)
df.set_index("i")[cols_time].plot(ax=ax[1], linewidth=1.0, logy=True)
fig.tight_layout()
fig.savefig("plot_bench_cpu.png")
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 3.702 seconds)