Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Quantile Regression¶
scikit-learn does not have a quantile regression. mlinsights implements a version of it.
Simple example¶
We first generate some dummy data.
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pandas import DataFrame
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from mlinsights.mlmodel import QuantileLinearRegression
X = numpy.random.random(1000)
eps1 = (numpy.random.random(900) - 0.5) * 0.1
eps2 = (numpy.random.random(100)) * 10
eps = numpy.hstack([eps1, eps2])
X = X.reshape((1000, 1))
Y = X.ravel() * 3.4 + 5.6 + eps
clr = LinearRegression()
clr.fit(X, Y)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 4))
choice = numpy.random.choice(X.shape[0] - 1, size=100)
xx = X.ravel()[choice]
yy = Y[choice]
ax.plot(xx, yy, ".", label="data")
xx = numpy.array([[0], [1]])
y1 = clr.predict(xx)
y2 = clq.predict(xx)
ax.plot(xx, y1, "--", label="L2")
ax.plot(xx, y2, "--", label="L1")
ax.set_title("Quantile (L1) vs Square (L2)")
ax.legend()
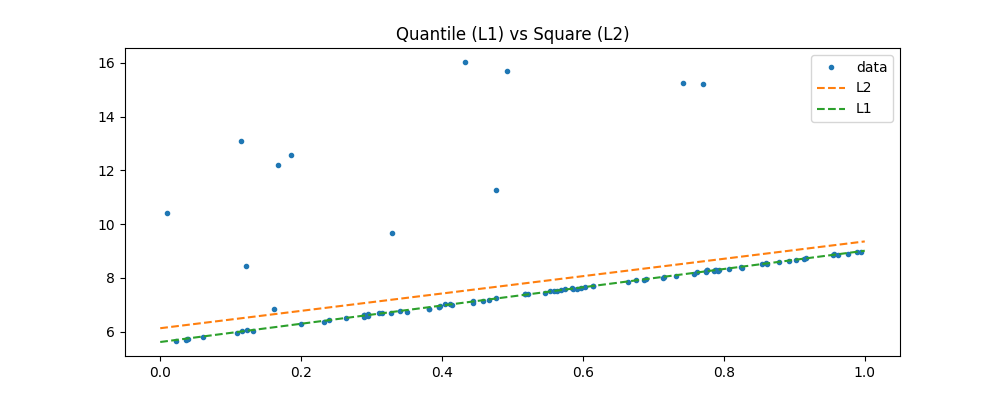
<matplotlib.legend.Legend object at 0x79fb8a322780>
The L1 is clearly less sensible to extremas. The optimization algorithm is based on Iteratively reweighted least squares. It estimates a linear regression with error L2 then reweights each oberservation with the inverse of the error L1.
clq = QuantileLinearRegression(verbose=True, max_iter=20)
clq.fit(X, Y)
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=1 error=797.5576249802946
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=2 error=506.8777296111872
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=3 error=464.8255055387572
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=4 error=464.21931630333637
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=5 error=463.76345090144736
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=6 error=463.43793901127776
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=7 error=463.27379019084043
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=8 error=463.13981872066677
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=9 error=463.019904893549
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=10 error=462.95038262760687
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=11 error=462.897059665222
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=12 error=462.86188319303875
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=13 error=462.8406599407556
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=14 error=462.82138530353166
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=15 error=462.80511418434753
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=16 error=462.7956115637766
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=17 error=462.7885385340178
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=18 error=462.7826260834315
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=19 error=462.7798826974612
[QuantileLinearRegression.fit] iter=20 error=462.7785977120451
0.4627785977120451
Regression with various quantiles¶
X = numpy.random.random(1200)
eps1 = (numpy.random.random(900) - 0.5) * 0.5
eps2 = (numpy.random.random(300)) * 2
eps = numpy.hstack([eps1, eps2])
X = X.reshape((1200, 1))
Y = X.ravel() * 3.4 + 5.6 + eps + X.ravel() * X.ravel() * 8
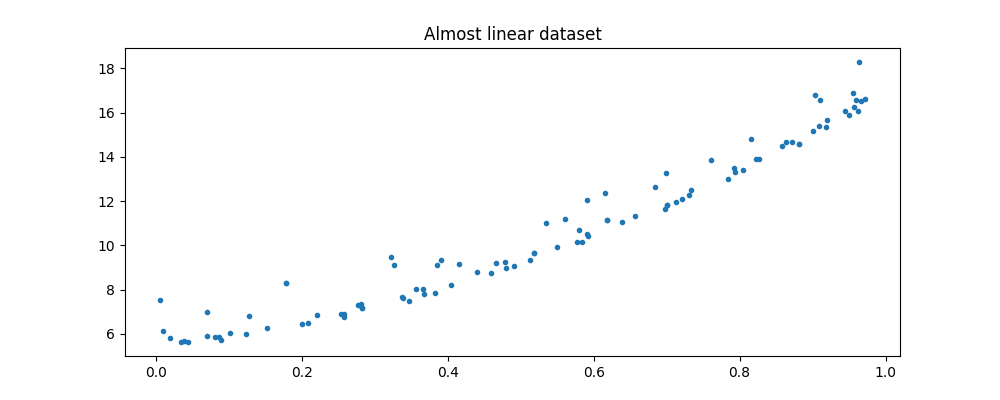
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Almost linear dataset')
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 4))
choice = numpy.random.choice(X.shape[0] - 1, size=100)
xx = X.ravel()[choice]
yy = Y[choice]
ax.plot(xx, yy, ".", label="data")
xx = numpy.array([[0], [1]])
for qu in sorted(clqs):
y = clqs[qu].predict(xx)
ax.plot(xx, y, "--", label=qu)
ax.set_title("Various quantiles")
ax.legend()
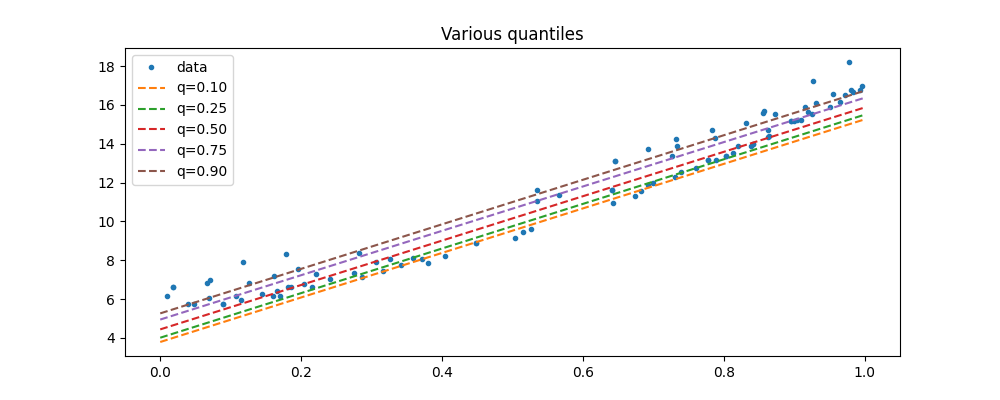
<matplotlib.legend.Legend object at 0x79fba1395fa0>
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.390 seconds)